
Mississippi Academic Assessment Program (MAAP)
Biology
PRACTICE TEST
Copyright © 2022 by the Mississippi Department of Education and Data Recognition Corporation. All rights reserved.
2022-2023
The Biology Practice Test is a useful tool for Mississippi educators to use in
preparing students for the format of the Mississippi Academic Assessment
Program for Science. The items were written and aligned to the 2018
Mississippi College- and Career-Readiness Standards for the Science. This
document contains 25 Biology items.
1
1. Adult somatic cell nuclear transfer, also known as cloning, may potentially be a method to
recover populations of endangered species. Recently, cloning was used on the last surviving
cow of a rare breed from New Zealand.
What is the strongest ethical and moral argument against continuing research and experiments
in cloning endangered species?
A. lack of mate selection for the cloned animals to reproduce
B. likelihood that cloned organisms would introduce new diseases to native species
C. possibilities that the process could be used on organisms for personal preference
D. concern that it will disrupt the economic market for individuals selling uncloned animals
2

2.
The chart shows the molecular structures of monomers associated with four common
macromolecules.
Record the label of each macromolecule listed below in the box next to its monomer molecular
structure.
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C H
HH H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
HH H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
HH H
H
C
H
C
H H
H
C
H
O
O
CH
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C H
HH H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
HH H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
HH H
H
C
H
C
H H
C O
O
CH
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C H
HH H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
HH H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
HH H
H
C
H
C
H H
C O
O
CH
OH
H
OH
H
OH
H
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
C
CC
O
C C
P O
_
O
O
_
O
OH
H
H
CH
2
H
H
H
O
N
H
CH
CH
C
O
N
C C
CH
2
SH
H
H
HHO
N
O
Name of
Macromolecule
Monomer Molecular Structure
Macromolecules and Their Monomer Structures
Labels
C
B
A
D
carbohydrate
lipid
nucleic acid
protein
3

Use the scenario to answer the next two questions.
Peppered Moths
Before the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain, birds fed primarily on dark-colored moths. The
Industrial Revolution caused environmental changes. Coal fires caused dark soot to be released
into the air. This soot was then deposited on trees, grasses, and buildings. This change to the
existing environment caused a change in the genetic frequencies demonstrated by moths in Great
Britain.
before Industrial Revolution after Industrial Revolution
Change in Peppered Moths
4

3.
Which graph best represents the genetic frequency of the dark-colored moths during the
Industrial Revolution in Great Britain?
A.
Time
Genetic Frequency
B.
Time
Genetic Frequency
C.
Time
Genetic Frequency
D.
Time
Genetic Frequency
5
4.
Based on the information in the scenario, what caused the change in the genetic frequencies
of the moths during the Industrial Revolution?
A. genetic mutations due to the soot
B. natural selection due to predation
C. chemical poisoning due to poor air quality
D. overproduction due to excess food sources
6
5.
Which two options identify contributions to cell theory that are attributed to Robert Hooke?
A. discovered and named cells
B. stated all plants are made of cells
C. observed cork cell walls under a microscope
D. determined all cells come from other preexisting cells
E. stated all cells have the same basic chemical composition
F. discovered that hereditary information is passed on from cell to cell
7

6.
All cells are either eukaryotic or prokaryotic.
Part A: Record the letter of an option in each box in the table to show whether the
characteristic describes a eukaryotic cell, a prokaryotic cell, or both types of cell. The options
may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic
and Prokaryotic Cells
OptionsType of CellCharacteristic
has membrane-bound organelles
has DNA in the cytoplasm
has a cell membrane
has ribosomes
prokaryotic
eukaryotic
both
1
2
3
Part B: The diagrams show a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryotic cell. On the diagram
representing the eukaryotic cell, select the structure where the cellular DNA is stored.
Cellular Structures
structure 1
structure 2
structure 3
structure 4
Cell 1 Cell 2
8
7.
Mitosis and meiosis are two processes that can produce new cells in an organism. Which
statement correctly compares and contrasts the new cells produced by each process?
A. New cells produced by mitosis have unique genetic material, and new cells produced by
meiosis have identical genetic material.
B. New cells produced by mitosis are responsible for reproduction, and new cells produced
by meiosis are responsible for growth and repair.
C. New cells produced by mitosis are the result of two nuclear divisions, and new cells
produced by meiosis are the result of one nuclear division.
D. New cells produced by mitosis maintain genetically identical offspring, and new cells
produced by meiosis contribute to genetic diversity in offspring.
9

8.
A student is comparing aerobic and anaerobic respiration in both animals and plants by
constructing equations to represent these four general chemical reactions.
Record the letters of the missing substances from the list below into the equations where they
belong. Some substances will be used more than once.
+ glucose + + energy
Aerobic Respiration in Animals
+ glucose + + energy
Aerobic Respiration in Plants
glucose + energy
Anaerobic Respiration in Animals
Anaerobic Respiration in Plants
glucose + + energy
ethanol
water
oxygen
lactic acid
carbon dioxide
A
B
C
D
E
10

9.
Under ideal circumstances in an environment, a population will grow exponentially. However, in
studies of actual populations in various environments, scientists have found that the
exponential growth rate a population may experience for a while will slow down and may
eventually level off at a constant rate. This is called logistic growth.
Exponential
Population Growth
Logistic
Population Growth
Time
Population Size
Time
Population Size
Which factor would most likely cause the growth rate of a population to shift from exponential
to logistic growth?
A. Predators that hunt the population are eliminated due to disease.
B. The birth rate in the population exceeds the death rate in the population.
C. The population consumes food resources as fast as they can be produced.
D. A competing population migrates to another area, leaving an excess of food and space.
11

10.
An incomplete diagram of a cell in a saline solution is shown. The concentrations of salt within
the cell and the solution are given.
Draw an arrow in the box inside the beaker to show the most likely direction of water flow and
record a label in the box below the beaker to best identify the type of movement occurring.
cell
(low salt
concentration)
saline solution
(high salt
concentration)
direction of
movement
Cell in a Saline Solution
type of movement:
Direction of
Movement
Type of
Movement
endocytosis
diffusion
active
transport
osmosis
4
1
2
3
12
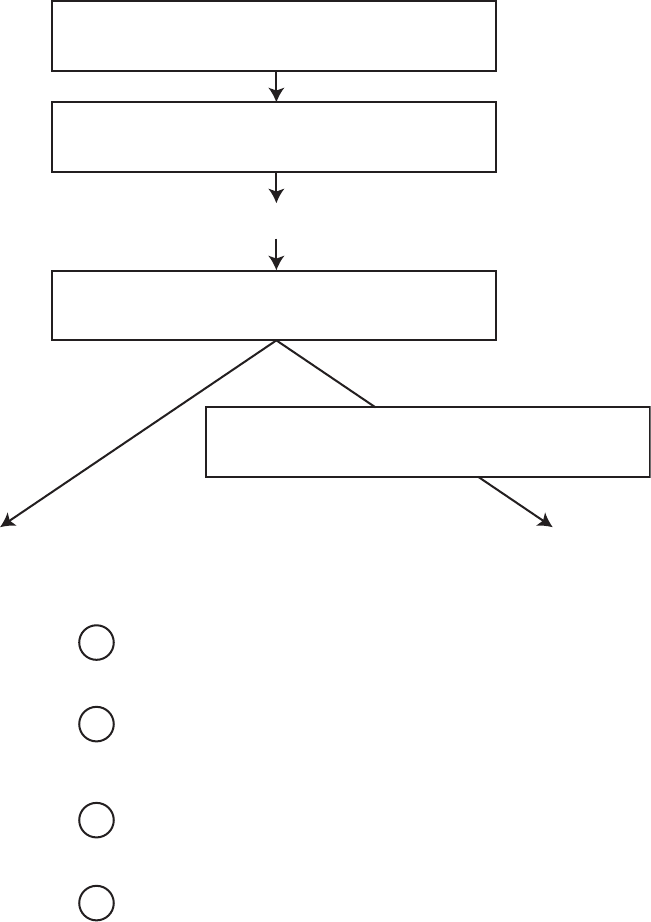
11.
The diagram shows an incomplete model of the evolution of heterotrophs and autotrophs.
Record the letter of a description in each box to correctly complete the model.
Evolution of Heterotrophs and Autotrophs
basic living cells
aerobic
heterotrophs
photosynthetic
autotrophs
evolution of structures that use
oxygen to break down sugars
evolution of structures that use
light energy to form sugars
formation of inorganic molecules
formation of organic molecules
W
X
Y
Z
13
12.
Which statement correctly compares viruses to bacteria?
A. Viruses are larger than bacteria, but both have a nucleus that contains genetic material.
B. Viruses are smaller than bacteria, but both have a nucleus that contains genetic material.
C. Viruses have a cell wall for protection, while bacteria are not surrounded by a cell wall.
D. Viruses have a protein capsule for protection, while bacteria are surrounded by a cell wall
and a cell membrane.
14
13.
Which step in cell division must occur first so that a young animal can grow into an adult?
A. The chromosomes must duplicate.
B. The chromosomes must separate.
C. The cells must divide the cytoplasm.
D. The cells must produce spindle fibers.
15

14.
The diagram models the flow of nitrogen through an ecosystem.
atmospheric
nitrogen (N
2
)
lightning
nitrates (NO
3
–
)
nitrites (NO
2
–
)
ammonium (NH
4
+
)
assimilation
ammonification
plants
denitrifying
bacteria
nitrifying
bacteria
nitrifying
bacteria
nitrogen-fixing
soil bacteria
nitrogen-fixing
bacteria
nitrification
decomposers
Nitrogen Cycle
Part A: Based on the diagram, which component is a direct product of abiotic and biotic
activities in this cycle?
A. nitrates
B. nitrites
C. ammonium
D. atmospheric nitrogen
Part B: What is the role of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in this cycle?
A. making atmospheric nitrogen available for plants
B. transforming sunlight energy into usable energy for plants
C. breaking down dead plant matter and releasing it as nitrogen into the atmosphere
D. increasing the amount of plant matter that decomposers can convert to ammonium
16

15.
Ensatina is a genus of salamander present along the western coast of North America. This
salamander is thought to have started in the wet environments of northern California and
southern Oregon (Oregon ensatina). From this location, the salamanders moved northward
into similar wet environments and southward into much drier environments. Over time, some of
the salamanders reached northern Mexico. The map shows the locations of different
subspecies of Ensatina.
Ensatina Salamanders over Time
Central
Valley
evolution
of western
population
evolution
of eastern
population
population split around the
Central Valley into western
and eastern populations
western and eastern
populations merged but
could no longer interbreed
original Oregon
ensatina population
moved southward
1
2
3
5
4
N
W
E
S
Which statement best describes the ensatina salamanders?
A. The southern movement of ensatinas resulted in salamanders that became more similar,
resulting in multiple subspecies becoming a single subspecies.
B. The northern movement of ensatinas resulted in a new subspecies of the salamander that
was able to survive in new and different environments.
C. The northern movement of ensatinas resulted in salamanders that were less similar as
their environments became drier and hotter.
D. The southern movement of ensatinas into drier, warmer environments that had less similar
salamanders resulted in a single subspecies becoming at least two different subspecies.
17
16.
Tapeworms attach themselves to the inner surface of the intestine in cows and consume some
of the passing food material before the cow can obtain the material’s nutrients. Which
statement best explains the role the tapeworm plays in relation to the cow?
A. The tapeworm is a predator because it lives inside of and attacks the cow.
B. The tapeworm is a competitor because it consumes nutrients the cow consumes.
C. The tapeworm is a commensalist because it cannot survive without a cow host to
protect it.
D. The tapeworm is a parasite because it benefits from living inside the cow and harms
the cow.
18

Use the scenario to answer the next two questions.
Red-Green Color Blindness
Red-green color blindness means that a person cannot distinguish shades of red and green. There
are no significant complications to being color-blind, however, affected individuals may be
prevented from holding certain occupations where color recognition is required. Males are affected
more often than females because the gene is recessive and located on the X chromosome.
Key
Color Blindness in Two Generations
affected
male
af
fected
female
unaffected
male
unaffected
female
I
II
19

17.
Study the female karyotype.
Female Karyotype
3 4 51 2
8 9 106 7
13 14 1511 12
18 19 2016 17
21 22 23
On which numbered pair of chromosomes would the gene for red-green color blindness be
located? Record the number on the line.
20

18.
Circle a number in each set of options to describe the possibilities for the offspring of a cross
between a female who is a carrier for color blindness and a male who is not color-blind.
There is a ( 0% / 25% / 50% / 75% / 100% ) chance the offspring will be a color-blind male.
There is a ( 0% / 25% / 50% / 75% / 100% ) chance the offspring will be a color-blind female.
21
19.
A student purchased a geranium plant from a greenhouse. The student uses the materials
listed below to transfer the geranium plant to a new container.
Materials
• 4,000 grams potting soil
• 5 grams fertilizer (contains nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium)
• 1 large clay flowerpot
• 1 mature geranium plant
• 1,000 milliliters water
• 2 worms
Which criterion and reasoning work together to correctly classify a material from the list as living or
nonliving?
A. Criterion: Living things have mass and volume, and nonliving things do not.
Reasoning: Since the soil has mass and volume, the soil is living.
B. Criterion: Nonliving things absorb water, and living things do not.
Reasoning: Since the flowerpot cannot absorb water, the flowerpot is living.
C. Criterion: Nonliving things reproduce, and living things do not.
Reasoning: Since the worms can produce offspring, the worms are living.
D. Criterion: Living things require nutrients, and nonliving things do not.
Reasoning: Since the geranium plant uses the fertilizer to grow, the geranium plant is living.
22

20.
A pedigree represents the inheritance of a particular trait through generations of individuals.
affected male
unaffected male
affected female
unaf
fected female
Key
3 6
1 3
721 54
2
1 2
I
II
III
Pedigree
Part A: Circle the inheritance pattern of the trait shown in the pedigree.
Based on the pedigree, the trait is most likely ( autosomal dominant / autosomal recessive /
sex-linked dominant / sex-linked recessive ).
Part B: What is the genotype of individual 3 in generation II?
A. AA
B. Aa
C. aa
D. X
A
X
a
E. X
A
Y
23
21.
Which statement best describes the ecological succession that takes place after a severe
wildfire?
A. Secondary succession takes place after a forest fire because only bare rock is exposed.
B. Secondary succession takes place after a forest fire because the affected land once
supported life.
C. Primary succession takes place after a forest fire because there is nothing living in or on
the affected land.
D. Primary succession takes place after a forest fire because land that was not previously
impacted by sunlight is exposed.
24

22.
The model shows the overall process of cellular respiration in a typical animal cell.
Cellular Respiration
2 31
2 ATP2 ATP 32 ATP
Part A: Circle a process in each set of options to identify the stages of cellular respiration.
Stage 1 is ( the citric acid cycle / the electron transport chain / glycolysis ).
Stage 2 is ( the citric acid cycle / the electron transport chain / glycolysis ).
Stage 3 is ( the citric acid cycle / the electron transport chain / glycolysis ).
Part B: Circle a reactant or product in each set of options to describe the processes shown
by the stages in the model.
Stage 1 uses ( carbon dioxide / glucose / oxygen ).
Stage 2 uses the products of stage 1
to produce 2 ATP and ( carbon dioxide / glucose / oxygen ).
Stage 3 uses the products of stage 2
and ( carbon dioxide / glucose / oxygen ) to produce 32 ATP and water.
25
23.
A student is developing a model of energy conversion during photosynthesis. Which
information must the student include in the model?
A. Light energy is transferred into glucose molecules as chemical energy.
B. Chemical energy is produced when glucose molecules are broken down.
C. Chemical energy is used to open chloroplasts so that light energy is collected.
D. Light energy is transferred into molecules of water and ATP as chemical energy.
26

24.
A cellular process is shown in the diagram.
Cellular Process
chromosomes
This process occurs in multicellular organisms and in single-celled organisms. The table
describes three examples of the process in different organisms.
Examples of Cellular Process in Organisms
Organism Use Outcome
strawberry
vegetative
propagation
produces two copies of the plant
sea anemone budding
produces a smaller copy of sea
anemone (polyp)
gecko regeneration
grows new tail after previous tail has
been removed
Using the information provided, which statement best describes the role of the cellular process
in different types of organisms?
A. The process allows cells to make exact copies in order to reproduce sexually or grow.
B. The process allows cells to make new versions in order to reproduce asexually or grow.
C. The process allows cells to make new versions in order to reproduce sexually or repair
cells.
D. The process allows cells to make exact copies in order to reproduce asexually or repair
cells.
27
25.
An original segment of DNA and a segment that has been mutated due to exposure to UV
radiation are shown below.
Original and Mutated DNA Strands
original segment:
mutated segment:
ATG
ATG
CCA
CCA
GGC
CGC
CCA
CCA
Part A: Which sequence represents the mRNA produced during transcription of the mutated
DNA segment?
A. UAC GGU GCG GGT
B. UAC GGU GCG GGU
C. AUC GGU GCG GGU
D. UAC CCU CCA GGU
Continued on Next Page
28

Part B: Refer to the mRNA codon chart below.
Second letter
First letter
U
U
C A G
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
Third letter
mRNA Codon Chart
Tyr
stop
stop
Cys
stop
Trp
UUU
UUC
UUA
UUG
Phe
Leu
UAU
UAC
UAA
UAG
UGU
UGC
UGA
UGG
UCU
UCC
UCA
UCG
Ser
Asn
Lys
Se
r
Arg
AUU
A
UC
AUA
AUG
Ile
Met
AAU
AAC
AAA
AAG
AGU
AGC
AGA
AGG
ACU
ACC
ACA
ACG
Thr
His
Gln
CAU
CAC
CAA
CAG
CCU
CCC
CCA
CCG
Pro
CGU
CGC
CGA
CGG
Arg
CUU
CUC
CUA
CUG
Leu
Asp
Glu
GA
U
GAC
GAA
GAG
GCU
GC
C
GCA
GCG
Ala
GGU
GG
C
GGA
GGG
Gly
GUU
GUC
GUA
GUG
Val
Which statement best describes this mutation?
A. The protein will not be produced; the mutation is a nonsense mutation.
B. The protein produced will not change; the mutation is a silent mutation.
C. The third amino acid in the protein would change from PRO to ALA, which may affect the
shape and function of the protein.
D. The third amino acid in the protein would change from ALA to PRO, which may affect the
shape and function of the protein produced.
29
This page is intentionally left blank.

Data Recognition Corporation
13490 Bass Lake Road
Maple Grove, MN 55311
Data Recognition Corporation
13490 Bass Lake Road
Maple Grove, MN 55311
Biology
Practice Test
END OF
COURSE

Biology Practice Test
Fall 2022
1
The information for each item, including the objective, DOK level, item type, and correct answer, is
located in this document. The items appear in the order as shown in the table.
Item
Number
Objective
DOK
Level
Item Type
Correct Answer
1
(BIO.3C.4) Research and identify how DNA technology benefits society.
Engage in scientific argument from evidence over the ethical issues
surrounding the use of DNA technology (e.g., cloning, transgenic
organisms, stem cell research, and the Human Genome Project, gel
electrophoresis).
2
Multiple
Choice
C
2
(BIO.1B.1) Develop and use models to compare and contrast the structure
and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and
RNA) in organisms.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
3
(BIO.4.4) Design models and use simulations to investigate the interaction
between changing environments and genetic variation in natural selection
leading to adaptations in populations and differential success of
populations.
2
Multiple
Choice
C
4
(BIO.4.5) Use Darwin's Theory to explain how genetic variation,
competition, overproduction, and unequal reproductive success acts as
driving forces of natural selection and evolution.
2
Multiple
Choice
B
5
(BIO.1A.2) Describe the tenets of cell theory and the contributions of Schwann,
Hooke, Schleiden, and Virchow.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
6
(BIO.1C.2) Investigate to compare and contrast prokaryotic cells and
eukaryotic cells, and plant, animal, and fungal cells.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
7
(BIO.3A.2) Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis in terms of
reproduction.
2
Multiple
Choice
D
8
(BIO.2.4) Conduct scientific investigations or computer simulations to
compare aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration in plants and animals,
using real world examples.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
9
(BIO.5.6) Analyze and interpret population data, both density-dependent
and density-independent, to define limiting factors. Use graphical
representations (growth curves) to illustrate the carrying capacity within
ecosystems.
3
Multiple
Choice
C
10
(BIO.1D.2) Develop and use models to explain how the cell deals with
imbalances of solute concentration across the cell membrane (i.e.,
hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic conditions, sodium/potassium pump).
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
11
(BIO.4.1) Use models to differentiate between organic and chemical
evolution, illustrating the steps leading to aerobic heterotrophs and
photosynthetic autotrophs.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
12
(BIO.1C.3) Contrast the structure of viruses with that of cells, and explain
why viruses must use living cells to reproduce.
2
Multiple
Choice
D
Biology Practice Test
Fall 2022
2
Item
Number
Objective
DOK
Level
Item Type
Correct Answer
13
(BIO.1E.2) Identify and describe the changes that occur in a cell during
replication. Explore problems that might occur if the cell does not progress
through the cycle correctly (cancer).
2
Multiple
Choice
A
14
(BIO.5.2) Analyze models of the cycling of matter (e.g., carbon, nitrogen,
phosphorus, and water) between abiotic and biotic factors in an ecosystem
and evaluate the ability of these cycles to maintain the health and
sustainability of the ecosystem.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
15
(BIO.4.6) Construct explanations for the mechanisms of speciation (e.g.,
geographic and reproductive isolation).
2
Multiple
Choice
D
16
(BIO.5.5) Evaluate symbiotic relationships (e.g., mutualism, parasitism, and
commensalism) and other co-evolutionary (e.g., predator-prey,
cooperation, competition, and mimicry) relationships within specific
environments.
2
Multiple
Choice
D
17
(BIO.3B.3) Investigate traits that follow non-Mendelian inheritance
patterns (e.g., incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles in
human blood types, and sex-linkage).
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
18
(BIO.3B.4) Analyze and interpret data (e.g., pedigrees, family, and
population studies) regarding Mendelian and complex genetic traits (e.g.,
sickle-cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, color-blindness, and
hemophilia) to determine patterns of inheritance and disease risk.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
19
(BIO.1A.1) Develop criteria to differentiate between living and non-living
things.
2
Multiple
Choice
D
20
(BIO.3B.4) Analyze and interpret data (e.g., pedigrees, family, and
population studies) regarding Mendelian and complex genetic traits (e.g.,
sickle-cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, color-blindness, and
hemophilia) to determine patterns of inheritance and disease risk.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key
21
(BIO.5.7) Investigate and evaluate factors involved in primary and
secondary ecological succession using local, real world examples.
2
Multiple
Choice
B
22
(BIO.2.3) Develop models of the major reactants and products of cellular
respiration (aerobic and anaerobic) to demonstrate the transformation of
the chemical energy stored in food to the available energy of ATP.
Emphasize the chemical processes in which bonds are broken and energy is
released, and new bonds are formed and energy is stored.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key

Biology Practice Test
Fall 2022
3
Item
Number
Objective
DOK
Level
Item Type
Correct Answer
23
(BIO.2.2) Develop models of the major reactants and products of
photosynthesis to demonstrate the transformation of light energy into
stored chemical energy in cells. Emphasize the chemical processes in which
bonds are broken and energy is released, and new bonds are formed and
energy is stored.
2
Multiple
Choice
A
24
(BIO.1E.3) Relate the processes of cellular reproduction to asexual
reproduction in simple organisms (i.e., budding, vegetative propagation,
regeneration, binary fission). Explain why the DNA of the daughter cells is
the same as the parent cell.
2
Multiple
Choice
D
25
(BIO.3C.3) Use models to predict how various changes in the nucleotide
sequence (e.g., point mutations, deletions, and additions) will affect the
resulting protein product and the subsequent inherited trait.
2
Technology
Enhanced
See Answer Key

Biology Practice Test
Fall 2022
4
Technology Enhanced Items
Answer Key
Item #2

Biology Practice Test
Fall 2022
5
Technology Enhanced Items
Answer Key
Item #5
Item #6
Part A
Part B

Biology Practice Test
Fall 2022
6
Technology Enhanced Items
Answer Key
Item #8
Item #10

Biology Practice Test
Fall 2022
7
Technology Enhanced Items
Answer Key
Item #11
Item #14

Biology Practice Test
Fall 2022
8
Technology Enhanced Items
Answer Key
Item #17
Item #18
Item #20

Biology Practice Test
Fall 2022
9
Technology Enhanced Items
Answer Key
Item #22
Item #25
Part A
Part B
