
Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) Engineer,
a Security Specialty within System Security Engineering
Abstract #23774
Holly Dunlap, Holly.Dunlap@Raytheon.com
Raytheon Missiles & Defense, System Security Engineering
Cyber SCRM Engineering SME
December 2021
© 2021 Raytheon Technologies Corporation.
All rights reserved.
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Agenda
• What is Cyber SCRM?
• Adversary
• Global Supply Chain Risks
• Customer Requirements
• Standards
• Future State Vision
• Integrating Cyber SCRM into RTX – It’s a journey.
• Raytheon Cyber SCRM Role & Responsibility
• Customer Program Perspective Example
• Key Takeaways
2
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Key Definitions
• Supply Chain Risk. The risk that an adversary may sabotage, maliciously introduce unwanted
function, or otherwise subvert the design, integrity, manufacturing, production, distribution,
installation, operation, or maintenance of a system so as to surveil, deny, disrupt, or otherwise
degrade the function, use, or operation of such system.
– DoDI 5200.44, Protection of Mission Critical Functions toAchieve Trusted Systems and Networks (TSN)
• Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management (C-SCRM) is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating the
risks associated with the distributed and interconnected nature of ICT product and service supply chains. It
covers the entire lifecycle of a system (including design, development, distribution, deployment, acquisition,
maintenance, and destruction) as supply chain threats and vulnerabilities may intentionally or unintentionally
compromise an ICT product or service at any stage of the lifecycle. Department Homeland Security (DHS)
• Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management (C-SCRM) is a systematic process for managing cyber supply chain
risk exposures, threats, and vulnerabilities throughout the supply chain and developing response strategies to
the cyber supply chain risks presented by the supplier, the supplied products and services, or the supply chain.
– DRAFT NIST 800-161 Rev 1, Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management Practices for Systems and Organizations
* ICT – Information Communication Technology
3
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

The Threat is Real…
The Adversary has moved from attacking our systems directly to attacking our supply chain.
Chinese DH-10
Russia’s A-50
U.S. HUMVEE
ALARM
TOMAHAWK
U.S. Reaper
Battlefield Losses: Yugoslav Museum of Aviation
China’s Yìlóng-1
These are Not Cooperative R&D Efforts
4
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management
The Global Suppl in presents th eatest attack surface to our national security systems.
CYBER
roelectronics is DOD's new No. 1 technology priority,
ping hypersonics to No. 3 – Inside Defense June 29, 2020
We are responsib he authenticity & integrity of the components integrated into our systems.
5
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Key Protection Activities to Improve Cyber Resiliency
Cyber SCRM Requirements are
derived from DoDI 5200.44
Program Protection & Cybersecurity
DoDI 5000.02, Enclosure 3 & 14
DoDM 5200.01, Vol. 1-4
DoDI 5200.39
DoDM 5200.45
DoDI 8500.01
DoDI 8510.01
DoDI 5200.44 DoDI 5230.24
Technology Components Information
What: A capability element that
contributes to the warfighters’
technical advantage (CPI)
What: Mission-critical functions
and components
What: Information about the
program, system, designs,
processes, capabilities and end-
items
Key Protection Activity:
• Software Assurance
• Hardware Assurance/Trusted
Foundry
Key Protection Activity:
• Anti-Tamper
• Defense Exportability Features
• CPI Protection List
Key Protection Activity:
• Classification
• Supply Chain Risk Management • Export Controls
• Anti-counterfeits
• Joint Federated Assurance
Center (JFAC)
• Information Security
• Joint Acquisition Protection &
Exploitation Cell (JAPEC)
• Acquisition Security Database
Goal: Prevent the compromise and Goal: Protect key mission
Goal: Ensure key system and
program data is protected from
adversary collection
loss of CPI
components from malicious
activity
Protecting Warfighting Capability Throughout the Lifecycle
Policies, guidance and white papers are found at our initiatives site: http://www.acq.osd.mil/se/initiatives/init_pp-sse.html
6
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Relationship of DoD Acquisition Policies and Industry
Best Practices often referred to as Standards
Supply Chain Risk Management
NIST SP 800-37
Applying the Risk Management
k (RMF) to Federal Information
Systems: A Security Life
NIST SP 800-160 Vol 1
Systems Security Engineering: Considerations for a
Multi-disciplinary Approach in the Engineering of
Trustworthy Secure Systems
Rev.2
NIST SP 800-53
NIST SP 800-161
Cyber
Security and Privacy Controls forInformation
Systems and Organizations
Supply Chain Risk ManagementPractices for
Federal Information Systems & Organizations
Rev.5
Draft Rev.1
CNSSI 1253
SECURITY CATEGORIZATION AND CONTROL SELECTION
FOR NATIONAL SECURITY SYSTEMS
NIST Internal Report 7622
Notional Supply Chain Risk Management
Practices for Federal Information Systems
Predicting future updates to include NIST SP 800-53 Rev 5
* Predecessor to NIST SP 800-161
7
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Raytheon Future State
Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management
Operational Systems of Systems
System Functional Decomposition
SwA Raytheon Vulnerability Assessment Process
(Guide & Enabler)
Supply Chain Trade Space Options
Assessments
Critical Components
Identification & Categorization
Management
Filtering
& Rating
Software /
Firmware (?)
(Hardware, Software, Firmware)
Internal Test Capability
Catalog & Guide
Hardware / Firmware
Test
Capability 1,2,3,4,5….
Applicable Type of Component
Level of Risk Mitigation
Architecture Internal
External
Internal
Design
Testing
Or External
Internal Risk Mitigation
Product Catalog
8
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
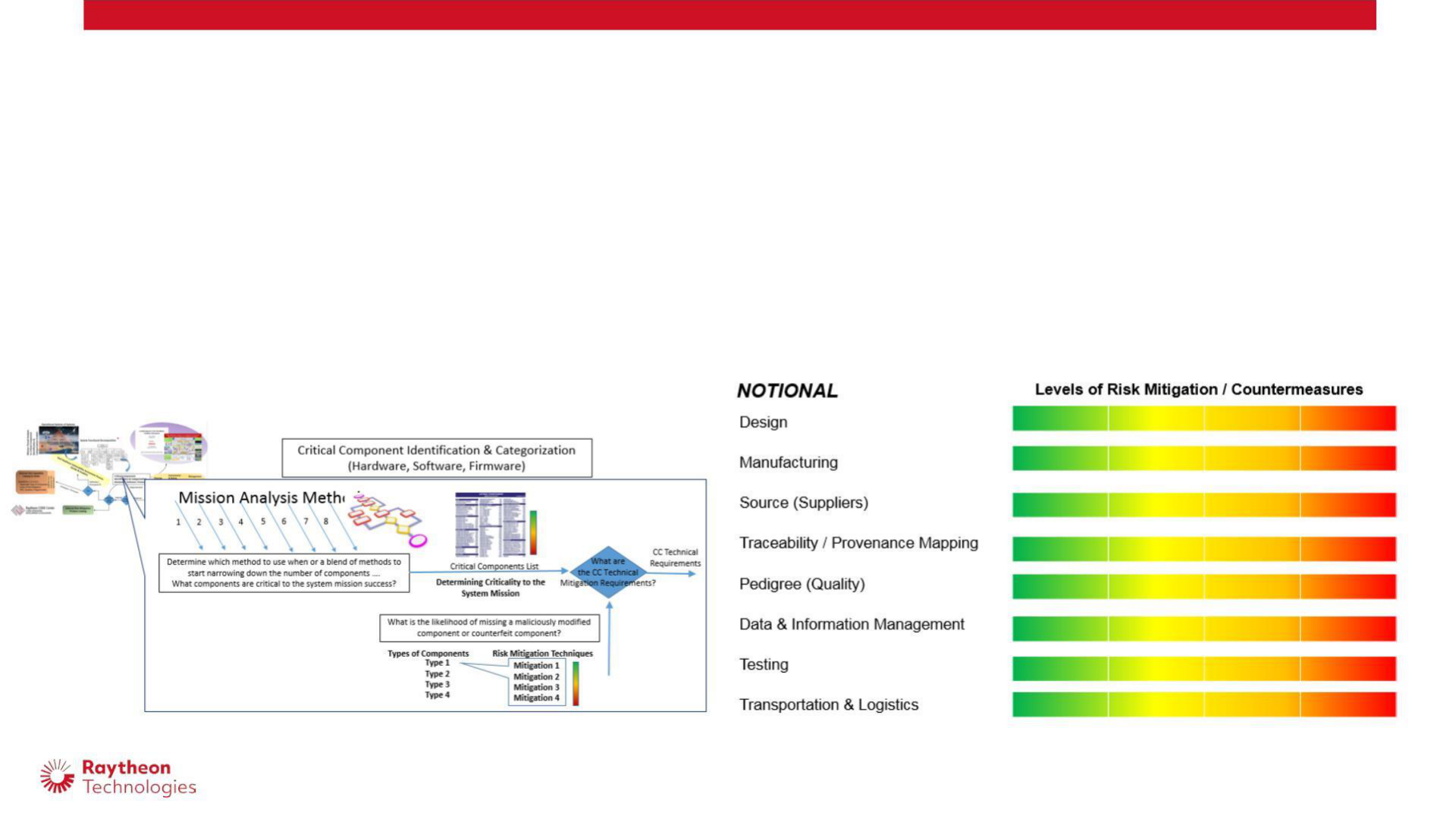
Catalog Trade Based Cyber SCRM Options
Programs need a range of risk mitigations to address supply chain risks for our System Mission Critical Components.
• Tiered Component Design Features
• Tiered Criteria andAudits for Levels of Security in Manufacturing
• Tiered Criteria and Evaluation of Suppliers
• Tiered Criteria for Critical Component Pedigree
• Tiered Requirements to Flow to Suppliers for How to Manage Data & Information
• Tiered Criteria and Options for Test Requirements and Evidence by the Type of Component
• Tiered Criteria and Options for Transportation & Logistics Mitigations.
9
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management
NIST SP 800-161
Supply Chain Risk Management Practices for Federal Information Systems & Organizations
Customer
Requirements
Initial System
Architecture
Initial System
Architecture
•
•
System Functions
Mission Threads
•
•
System Functional
Capability
CONOPS
Program protection implementation is
an iterative process that matures over
the lifecycle.
RTN Security
Architecture Framework
PPiP
•
•
•
•
•
AT
SCRM
Cybersecurity
OPSEC
SwA
Provides approach and
levels of risk mitigation
(countermeasure
options)
Countermeasure
Selection
Identify & Assess Assess System
Security Risk
Evaluate
Trades
Criticality
Implement
• CPI – Risk = Consequence x
Exposure
Mission Critical Information
Mission Critical Functions
•
•
CPI Identification (Technology)
Mission Critical Information –
Cybersecurity
Mission Critical Functions –
Trusted Systems & Networks
(SCRM & SwA)
• Risk Reduction
(Countermeasures)
Cost
Schedule
Performance
•
•
•
•
•
Validate
& Verify
•
• Components
•
•
Hardware
Software
Likelihood
Risk
Residual
Risk
https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-161/final
Raytheon
Program Protection
Threats
Consequence
10
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Raytheon's Integrated Supply Chain Construct
Integrate Cyber SCRM Considerations into Existing Raytheon Supply Chain Methods and Tools
11
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Raytheon’s Cyber SCRM Role OV-1
Enterprise Team
Supplier
Management
Supplier
Assessments
Program
Subcontract
Lead
Supply Chain
Operations
Contracts
(Ts & Cs)
Program Team
Quality Components Safety Reliability
Engineer Engineer Engineer Engineer
SC Tools,
Processes,
Methods
The Cyber SCRM Engineering Lead is responsible for the
program strategy and technical subsystem and component
procurement and subcontracting requirements to address global
supply chain risks.
•
•
•
•
•
•
Cyber SCRM Strategy
System Mission Criticality Analysis for Logic Bearing Critical Component Identification
Bill of Materials Decomposition
Mitigation Evaluation for Procured and Subcontracted Material and Software.
Supplier / Sub Selection Criteria for Cyber SCRM Considerations
Cyber SCRM Asset Management Considerations
Material Program
Manager (MPM)
SC Cyber
SCRM
Engineer ??
SC Cyber
SCRM
DFARS
Cyber SCRM
Engineer
Cyber SCRM Engineer Addresses Global Supply Chain Risks to Program Procurements
13
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Example Raytheon Program Cyber SCRM Perspective
Holly Dunlap
ProgramArchitecture
Program System Design
Security Focus
Leads the holistic approach for integrating and managing the security
risks. Develops a security view within the system architecture.
PPiP (SSE)
Works with System Chief Architect and System Design
Engineers to address Security related requirements via an
iterative process
System Mission Criticality Analysis (incorporates safety & reliability) Results
System Mission Critical Function & System Mission Critical Component
Approach to the
development of
software
Supply Chain Risk
Management Plan
Cybersecurity Software
Development Plan
Works with Chief Engr, SSE, Cybersecurity Lead,
and relevant Program SMEs to identify Critical
Program Information (CPI) and inherited CPI.
Information
protection strategy
Anti-tamper Plan
Strategy
Material Program Strategy
Develops a plan on how to protect CPI.
add to the critical
rity requirements are
r statements of work
Cyber SCRM requires coordination & collaboration with other security
specialties as well as other program plans. It is not necessarily straight forward
and it is not necessarily consistent from program to program regarding which
plans must be coordinated.
Rayt
-notes
WE – Counterfeit Material and Malware Avoidance
Process Requirements.
COTS (GOTS / FOSS)
Management Plan
Coordinates an manages security related technical
requirements to include risk mitigations for subcontractors
and suppliers
AW – Software Quality Assurance Program
Counterfeit
Components Plan
Patch & Vulnerability
Management Plan
GP - Electronic Part and Assembly Counterfeit Risk
Mitigation
Microelectronics Source
Protection Plan
Continuous Monitoring
UK – Certificate of Conformance
Raytheon’s Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management Program Plan Relational Mapping
14
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
Distribution Statement A- Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.

Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management
Key Takeaways
• Adversaries are moving from directly attacking our systems to attacking our more
vulnerable supply chains.
• Cyber SCRM is a new and developing security specialty discipline within System
Security Engineering and Systems Engineering
• Apartnership between Engineering, MissionAssurance, and Supply Chain
organizations is an imperative.
• Cyber SCRM contributes to a holistic approach to program protection and a
Program Protection implementation Plan (PPiP).
15
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.

References:
• DoDI 5200.44
– https://www.esd.whs.mil/Portals/54/Documents/DD/issuances/dodi/520044p.pdf?ver=2018-11-08-075800-903
• NIST SP 800-53 Rev 5
– https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-53r5.pdf
• NIST SP 800-160
– https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-160v1.pdf
• NIST SP 800-161
– https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-161/rev-1/draft
• Deliver Uncompromised,AStrategy for Supply Chain Security and Resilience in Response to the
Changing Character of War
– https://www.mitre.org/sites/default/files/publications/pr-18-2417-deliver-uncompromised-MITRE-study-26AUG2019.pdf
16
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.

Questions?
17
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.

Holly Dunlap Bio
• BS Electrical Engineering & MBA
• 10 years Nuclear Weapons, National Nuclear SecurityAdministration (NNSA) Kansas City Plant, M&O Honeywell
– 3 Year Rotational Leadership Development Program (10 years experience in 3 years)
•
•
•
Program Manager of B83
Supply Chain 18 months (Rotated every 3 months)
Intelligence Community (Reverse Engineering, Rapid Fielding, Analysis)
– Certified 6 Sigma Black Belt – Microelectronics
• OSD DDR&E Technical Intelligence, Pentagon +4 years
– Emerging & Disruptive Technology. Investment strategy to ensure US technical capability advantage. Work intimately with Anti-tamper ExecutiveAgent, National &
Defense Intelligence Community, and Defense System Developers. Strategic 15 – 20 Year Planning.
• Ktech LaterAcquired by RTN RMS
– USD(I) Contract Supply Chain & Logistics LayeredAnalysis; Data & Information Exploitation. 18 month effort.
• RMS – IDS – RMD (+15 years)
– NDIA System Engineering Division Elected Chair (+13 Committees, +500 members; government, industry, academia, FFRDC)
– NDIA System Security Engineering Committee Chair, +9 years
– Raytheon Systems Engineering Council – Cyber Resiliency & System Security Project Lead
– Cyber Enterprise Campaign
– Cyber Operations Development & Evaluation (CODE) Center
– PI Security & Trustworthy Foundations for Electronics Resurgence (STryFER) IDIQ Contracted Research & Development (CRAD) Proposal
18
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.

Thank you.
19
This document does not contain technology or technical data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations.
