
1. Verbs
Read the following sentences.
The teacher writes on the blackboard.
The singer sings the song.
My neighbors live in Delhi.
Aman exercises regularly.
The child cries bitterly.
Identify the action words from the list given below.
Chair, play, hit, ball, sweet, look, run, go, dance, hare,
Here, two, made, words, action, express, tell, flowers.
Verbs can be divided into two categories.
1. Main verb
2. Helping verb
Main verb- The main verb of the sentence shows action.
The mothers are fighting a battle each day.
We will water the plants soon.
The birds were chirping.
He showed us the way to the hospital.
The words underlined in the sentences given above are
called action words. They show the work being done.
Such words are known as verbs.

In the above examples the underlined verbs show the action being performed
and hence are known as main verbs.
Helping verb- The helping verbs work along with the main verb to
complete the sentence. They also denote the time of an action. They are
also known as auxiliaries.
Radha is watching television.
Why are you late for school?
The kitchen was cleaned last night.
The laptop is working fine.
In the above examples the underlined verbs assist in sentence completion.
They are known as helping verbs.
Identify the main verb and the helping verb from the sentences below.
The boy had gone to the market when I called.
I am reading a story.
She washes the car. She was sleeping earlier.
We would love to go out with them.
They shall obey their elders.
Underline the verbs in the sentence.
Lions roar loudly.
The sun was shining brightly.
Don’t go out. It is raining.
We will visit Dubai next year.

The patient was admitted to the hospital.
Finite & Non-finite verbs
The main verbs which change their form according to the subject of the
sentence are known as finite verbs.
The old man walks slowly.
My grandparents walk hurriedly.
In the above examples, the verb walks changes its form according to
to the subject (old man & grandparents). Therefore, walk is a finite
verb.
Non-finite verbs are not the main verbs of the sentence. They do not
demonstrate the time of action and do not change their form according to the
subject. Often, they are used as nouns, verbs or adjectives.
Swimming is my favorite sport.
We like to buy gifts.
In the above examples, the verbs swimming & buy do not change
their form according to the subject and hence are non-finite verbs of
the sentence.
Identify whether the verb is a finite verb or a non-finite verb.
The cobbler mends my shoes.
Crying over the spilt milk is of no use.
The manager scolded the children.
Carefully read your lesson & answer the question.
Non-finite verbs can we sub-divided into three categories.
1. The infinitive: to drink, to buy, to go, to arrange, to love
2. The participle: writing, reading, growing, learning (present participle)
Stolen, grown, read, became, decided (past participle)
3. The gerund: stealing, living, jumping, typing
Identify the type of non-finite verb.
I would love to have coffee.
Exercising is good for health.
The farmer has grown beautiful plants.
I want to dance.
Listening is an art.
Transitive & Intransitive verbs
The verbs followed by a direct object are called transitive verbs.
Ex- She wrote a book.
In the above example, the verb wrote is followed by a direct object book.
Hence, it is a transitive verb.
Now, let’s see another example.
Ex- He ate.
In the above example, the verb ate has no object. Hence, it is an intransitive
verb.
The verbs which are not followed by a direct object are called intransitive
verbs.
Identify whether the verb is transitive or intransitive.

I waited for long.
He bought me a cup of coffee.
The puppies littered.
I was disturbed by a loud noise.
He gave me the book.
Tenses

We can divide time into three categories.
The present (happening now)
The past (happened earlier)
The future (will happen)
Tenses denote the time when the action is performed.
The baker bakes the cake. (Present)
The police caught the murderer. (Past)
We will travel to London next month. (Future)
Simple present tense
Read the following sentences.
I like coffee.
Raman goes for a walk daily.
The sun sets in the west.
The bees suck nectar from the flowers.
The action words in the sentence given above are conjugated in simple
present tense.
Simple present tense is used to-
Express habitual actions
Make general statements
Talk about scientific truths/ universal actions

Rule – Add s/es to the root form of the verb
Singular
Subject
Plural verb
Plural Subject Singular verb
I / You Singular verb
I brush my teeth.
In this sentence, I is the subject and therefore it takes the form ‘brush’.
Kapil waters the plants.
In this sentence, Kapil is the subject and therefore it takes the form ‘waters’.
The teachers teach the class.
In this sentence, teachers is the subject and therefore it takes the form ‘teach’.
Complete the blanks with simple present tense.
My daughter ______ me every day. (greet)
The schools _______ on Sunday. (close)
I _____ very slowly. (walk)
You _____ the secrets. (keep)
Observe the following sentences now.
She does not like playing.
Do you know them?
Does the child cry?
We do not make much mistakes.
Negative Present tense SUBJECT + DO/DOES NOT +
FIRST FORM OF THE VERB
Interrogative Present tense DO/DOES + SUBJECT + FIRST
FORM OF THE VERB
Always remember, the negative & interrogative form of the present tense will
always be formed using the first form of the verb.
Change the following into negative.
They go to the park.
My parents clean the room.
She writes beautiful stories.
You make funny faces.
Change the following into interrogative.
Raghav catches the ball.
The player injures himself.
She switches off the lights.
The boy watches television.

Present continuous tense
Read the following sentences.
I am writing a letter.
A young boy is smiling at the stranger.
My dad is leaving for Chandigarh.
The verbs marked in bold represent the present continuous form of the verb.
Present continuous tense is used to describe the actions which are taking
place at the moment of speaking.
Is / am/ are + Ing form of the verb
Give the -ing form of the following verbs.
Decide
Grow
Bring
Shine
Eat
Whenever a verb ends in -e, we drop the e & add -ing to make the -ing
form of the verb.

Negative Present continuous Subject + is/am/are +not + -ing form
of the verb + object
Interrogative Present continuous Is/am/are + subject + -ing form of
the verb + object
Complete the sentences using present continuous tense.
The teacher _________________ on the blackboard. (write)
I ________________ to leave. (plan)
Ram and his friends ___________ the homework. (discuss)
The little boy ________the truth. (tell)
The animals ______ on the road. (walk).
Change the sentences into negative & interrogative present continuous form.
The boy is reading a book.
The police is investigating the case.
The children are making a lot of noise.
The birds are flying in the sky.
I am having my breakfast.

Simple past tense
Read the following sentences.
He helped me with my lesson.
I played a hockey game.
She broke the flower pot.
The box contained precious items.
The action words in the sentence given above are conjugated in simple past
tense. Simple past tense is used to describe the actions which have already
taken place before the time of talking.
To conjugate a verb in past tense, ed is added to the main verb or second
form of verb is used.
Put the verbs given in brackets in simple past tense.
He _______ me an invitation. (send)
I ______ to give my exams. (decide)
Sonu ______ his baseball cap. (love)
We ____ the truth. (tell)
Ruchika ______ the match. (win)
Negative Past tense SUBJECT + DID NOT + FIRST
FORM OF THE VERB
Interrogative Past tense DID + SUBJECT + FIRST FORM
OF THE VERB

Always remember, the negative & interrogative form of the past tense will
always be formed using the first form of the verb.
Change the following into negative.
They go to the gym.
My parents arrange the room.
She weaves beautiful stories.
You drew a beautiful picture.
Change the following into interrogative.
He chooses the red one.
It costs 400 rupees.
I keep all my cupboards clean.
He shut the door.
Verb Past tense
Go Went

Choose Chose
Read Read
Put Put
Cost Cost
Let Let
Broadcast Broadcast
Write Wrote
Give Gave
See Saw
Keep Kept
Eat Ate
Bring Brought
Buy Bought
Begin Began
Bend Bent
Shut Shut
Beat Beat
Blow Blew
Catch Caught
Build Built
Drink Drank
Dig Dug
Draw Drew
Drive Drove
Fell Fall
Dream Dreamt

Feed Fed
Feel Felt
Find Found
Fight Fought
Fly Flew
Forget Forgot
Get Got
Hide Hid
Hit Hit
Hold Held
Hurt Hurt
Know Knew
Lay Laid
Let Let
Lose Lost
Make Made
Put Put
Quit Quit
Pay Paid
Meet Met
Ride Rode
Ring Rang
Run Ran
Rise Rose
Sell Sold
Send Sent

Set Set
Shoot Shot
Shake Shook
Sink Sank
Shrink Shrank
Sleep Slept
Spend Spent
Spill Spilt
Spread Spread
Stick Stuck
Swing Swang
Swim Swum
Think Thought
Throw Threw
Understand Understood
Wake Woke
Arise Arose
Wear Wore
Win Won
Write wrote
Past continuous tense

Read the following sentences.
I was talking to my friend.
The books were lying on the table.
The maid was dusting the floor.
The verbs marked in bold represent the past continuous form of the verb.
Past continuous tense is used to describe the actions which took place in
continuation sometime in the past.
Was/ were + Ing form of the verb
Give the -ing form of the following verbs.
Check
Hop
run
give
ride

Negative Past continuous Subject + was/were +not + -ing form
of the verb + object
Interrogative Past continuous Was/were + subject + -ing form of
the verb + object
Complete the sentences using past continuous tense.
Parul ________ a pack of chips. (buy)
Sonal & her friends ________ for a picnic. (go)
It ________ heavily. (rain)
The trees _________ in the air. (sway)
We _________ our lunch. (enjoy)
Change the sentences into negative & interrogative past continuous form.
The teacher scolds the children.
The cat hid behind the door.
The boy holds the pen.
He made a birthday card.
Simple future tense
Look at the sentences given below.

The train will arrive at 5pm.
I will go to the park today evening.
I will have my dinner soon.
The verbs marked in bold represent the simple future form of the verb.
Simple future tense is used to describe the actions that would take place in
the time to come.
To conjugate the verb in simple future tense, will or shall is used along with
the root form of the verb.
Rule- Will/ shall + V1 (root form of the verb)
Fill in the blanks with simple future tense.
We _________ all our friends for dinner. (invite)
He _________ calligraphy. (learn)
The colleges ___________ soon. (resume)
India __________ the vaccine soon. (discover)
Negative future tense SUBJECT + WILL/SHALL + NOT
+ FIRST FORM OF THE VERB
Interrogative future tense WILL/ SHALL + SUBJECT +
FIRST FORM OF THE VERB
Change the following sentence into negative.

The girl wears a long dress.
He marries his girlfriend.
His team comes late.
The car cleaner washed my car.
Madhur is studying in his room.
Change the following sentences into interrogative.
They will create a video.
He will have a team meeting.
Jia will give her Math test.
The driver will drive the car.
It will rain tomorrow night.
Future continuous tense
Read the following sentences.

I will be learning guitar soon.
They will be working hard.
The maid will be washing the clothes.
The verbs marked in bold represent the future continuous form of the verb.
Future continuous tense is used to describe the actions which will take place
in continuation sometime in the future.
Rule- will/shall + be + ing form of the verb.
Negative Future continuous Subject + will/shall+ not + be + -ing
form of the verb + object
Interrogative Future continuous Will/shall + subject + be + -ing
form of the verb + object
Complete the sentences using future continuous tense.
I ________ to bed soon. (go)
He ________ money from the bank soon. (withdraw)
They __________ their lunch. (finish)
He __________ next week. (visit)
The University _________ the results soon. (declare)
Change the sentences into negative & interrogative future continuous form.
The teacher scolds the children.
I will take bath in the evening.

They go to office.
Next year, I will marry him.
He waited at the bus stop.
Present perfect tense
Read the following sentences.

I have received your message.
He has had bath lately.
Mahima has just left the room.
The verbs marked in bold represent the present perfect form of the verb.
Present perfect tense is used to describe an action which was completed in
the past but the results of which can be seen in the present.
Rule- has/have + 3
rd
form of the verb.
Complete the sentences using present perfect tense.
He _________ already _______. (arrive)
I __________ the letter yet. (write)
The boy __________ his file. (submit)
We ________ to Agra. (be)
It _________ to rain. (start)
Verb Third form
Go Gone
Choose Chosen
Read Read
Put Put
Cost Cost
Let Let
Broadcast Broadcast

Write Written
Give Given
See Seen
Keep Kept
Eat Eaten
Bring Brought
Buy Bought
Begin Begun
Bend Bent
Shut Shut
Beat Beaten
Blow Blown
Catch Caught
Build Built
Drink Drunk
Dig Dug
Draw Drawn
Drive Driven
Fell Fallen
Dream Dreamt
Feed Fed
Feel Felt
Find Found
Fight Fought
Fly Flown
Forget Forgotten

Get Got
Hide Hidden
Hit Hit
Hold Held
Hurt Hurt
Know Known
Lay Laid
Let Let
Lose Lost
Make Made
Put Put
Quit Quit
Pay Paid
Meet Met
Ride Ridden
Ring Rung
Run Run
Rise Risen
Sell Sold
Send Sent
Set Set
Shoot Shot
Shake Shaken
Sink Sunk
Shrink Shrunk
Sleep Slept

Spend Spent
Spill Spilt
Spread Spread
Stick Stuck
Swing Swung
Swim Swum
Think Thought
Throw Thrown
Understand Understood
Wake Waken
Arise Arisen
Wear Worn
Win Won
Write Written
ADJECTIVES

Adjectives are words we use to describe a noun or pronoun. It is a word
which qualifies (shows how big, small, great, many, few, etc.) a noun or a
pronoun is in a sentence.
Ram is a tall boy.
Hari is a strong player.
Avi has a brown dog.
Identify the adjectives,
He carried a heavy bag.
Aman is a sincere boy.
The girl was in a cheerful mood.
The teacher told us a story of a greedy dog.
The class was noisy.
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate adjective.
He is a ______ boy.
The teacher gave us _____ problems to solve.
The fruit tasted _______.
My sister works in a _____ office.
The _____ lamb hid behind the door.

Degrees of Comparison.
1. Positive degree.
2. Comparative degree.
3. Superlative degree
Ram is a tall boy.
Hari is taller than Ram.
Avi is the tallest of the three.
The Adjective ‘tall’ is in the Positive Degree. Positive Degree is used when no
comparison is made i.e. when we speak about only one person or thing.
The Adjective “taller” is said to be in the Comparative Degree. It represents
a higher degree of the quality than the Positive. It is used to compare the
qualities of two persons or things. Here height of Hari and Ram are
compared and shows the difference of quality between the two.
The Adjective “tallest” is said to be in the Superlative Degree. It represents
the highest degree of the quality. It is used when more than two objects are
compared.
Degrees of adjectives
Positive Comparative Superlative
Happy Happier happiest
Merry Merrier merriest
Lazy Lazier laziest
Heavy Heavier heaviest
Costly Costlier costliest
Fat Fatter fattest
Hot hotter hottest
Big bigger biggest

Degrees of comparison for irregular adjectives
Fill in the blank with appropriate degree of comparison.
This sum was ________ than the earlier one. (simple)
He scored _______ marks. (good)
His mother is the ___________ of all. (courageous)
Cheetah is the ___________ animal. (fast)
Sad sadder saddest
Positive Comparative Superlative
good/well better best
Little less least
Much more most
Old older oldest
elder eldest
Bad worse worst
evil/ill worse worst
Ill worse worst
Far farther farthest
Well better best
Late later latest
Many more most
Near nearer nearest
In inner inmost/inner most
Out outer/utter utmost/utter most

His house is _______ from mine. (far)
Note:
“Than” is used after the Comparative Degree. “The” is used before
the Superlative Degree.
Do not use the Double Comparative and Superlative, such as more better
and most loveliest.
A few Comparative are followed by “to”, instead of than; as, inferior to,
superior to, junior to, senior to.
Each, every, either, neither, when used as Adjectives, go with singular Noun.
Example- Every boy was punished.
Types of adjectives
Adjectives of quality such as honest, strong, sincere, easy, difficult.
Adjectives of quantity such as some, much, more, any
Adjectives of number such as one, three, millions, two
Demonstrative adjectives such as this, that, these, those
Interrogative adjectives such as which, whose, when
Nouns
Nouns are naming words.
The name of a person, place, animal or thing is called a NOUN.
EG: 1. Ram is planning a trip to Goa with his friends and his dog.
2. Kush bought a chocolate for his brother.
Identify the nouns in the given sentences-
1. The door of the house is locked.
2. France is a beautiful country.
3. Ravi and Rajesh are brothers.
4. Give me a glass of water.
5. Neeraj has a pet dog named Tuffy.
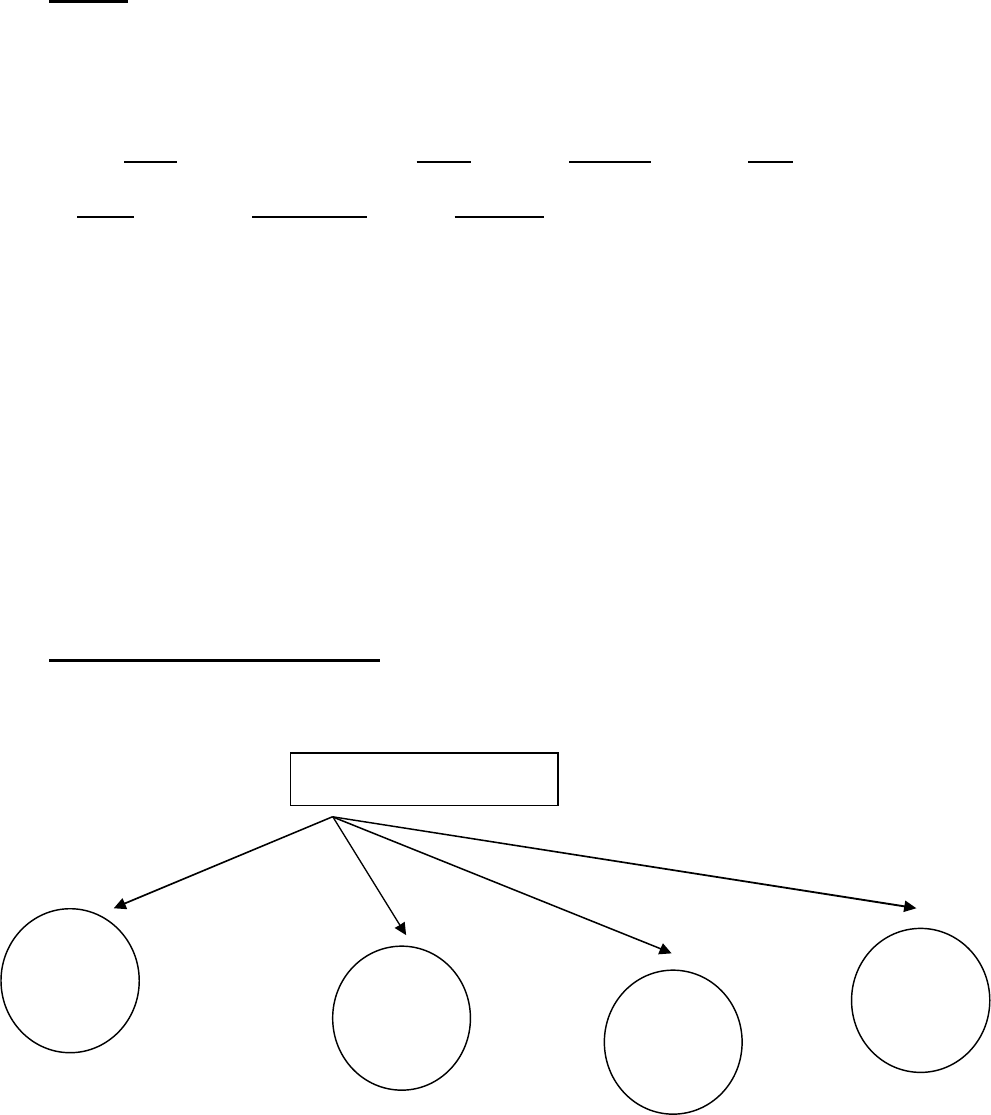
CLASSIFICATION OF NOUNS
NOUNS
Commo
n
Nouns
Proper
Nouns
Collectiv
e Nouns
Abstra
ct
Nouns

Common nouns: Nouns which refer to things in general. Eg: boy, bed, river
etc.
Proper nouns: Nouns which refer to a particular thing, place or person. Eg:
Amrita, Delhi, Yamuna etc
Girl Amrita
Boy Varun
River Ganga
Classify the following as common nouns or proper nouns-
1. Jatin likes to fly kites during leisure time.
2. My brother lives in Mumbai.
3. Hetal likes to eat pancakes and bread
4. Chandigarh is also called the pink city.
5. Black is my favourite colour.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMMON NOUNS
Countable nouns: Nouns which can be counted. Eg: pen, eraser, cars etc
Uncountable nouns: Nouns which cannot be counted. Eg: milk, rice, water etc
PRACTICE EXCERCISE-
Identify the following as countable or uncountable nouns-
1. Sweets- 12. Bed-
2. Books- 13. Curtain-
3. Sugar- 14. Juice-
COUNTABLE
NOUNS
UNCOUNTABL
E NOUNS

4. Hair- 15. Chair-
5. Milk-
6. Pen-
7. Money-
8. Bread-
9. Loaf of bread-
10.Laptop-
Further we have two more classifications of nouns:
Nouns which talk about things as a whole or a group are called collective nouns.
A herd of sheep
A galaxy of stars
A tuft of grass/hair
A collection of stamps
A band of musicians
(Practice exercise and list to be included)
Nouns which can only be felt and cannot be seen or touched are called
abstract nouns.
Bravery
Childhood
Peace
Wisdom
Nouns which can be seen or touched or felt are called concrete nouns.

Box
Children
Notebooks
Refrigerator
PRACTICE EXERCISE
Underline the abstract nouns and circle the concrete nouns-
1. Even though the weather was bad, she had hope that the train would
reach the station on time.
2. Rekha has spent the entire childhood in struggle.
3. A friend in need is a friend indeed.
4. Cleanliness is the key, my mother practices at home.
5. Our parents have always taught us to work with honesty.
NOUNS – GENDER
On the basis of gender nouns can be classified into four categories-
1. Masculine gender
2. Feminine gender
3. Common gender
4. Neuter gender

Boy Girl
Father Mother
Son Daughter
Uncle Aunt
Servant Maid
Man Lady
Actor Actress
Monk Nun
Brother Sister
Bachelor Spinster
Duke Duchess
Emperor Empress
Husband Wife
God Goddess
Host Hostess
King Queen

Male Female
Nephew Niece

Nouns possession
Observe the sentences given below.
The boy’s home is clean.
The teacher’s hair is very long.
The apostrophe s in the above sentences show belongingness/ possession.
It shows that the things are related to one another.
To show possession ‘s is added to the noun to which the particular thing
belongs.
Write the expressions given below to demonstrate possession.
The house of the lieutenant.
The book of the child.
The purse belonging to my mother.
The room in which my brother sleeps.
The poem written by Suman.
Rewrite the sentences given below using ‘s
He sat on the chair of the manager.
Ruhi bought a charger for the laptop.
He kept the shoes of Rashi in the closet.
He brought the chocolates made by Ankita.
The uniform of the child was dirty.

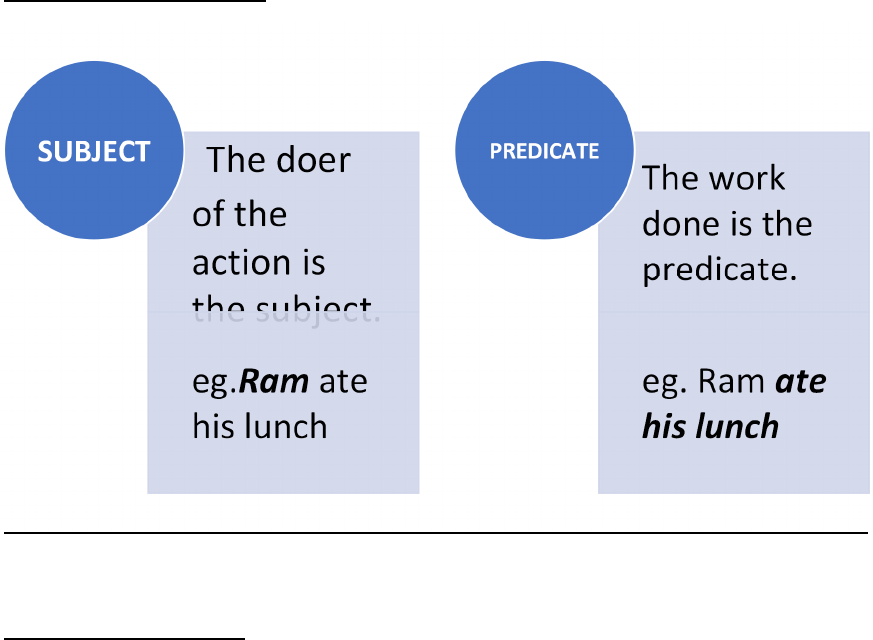
SENTENCES
A sentence is a
Group of words
Have a meaning
Make complete sense
Eg: We go to London every year.
He is an intelligent boy.
√ Group of words
√ Have a meaning
√ makes complete sense
Therefore, it is a sentence
Phrase
A phrase is a
Group of words
Makes some sense
But have an incomplete meaning
Eg: Get out
Bring him here
√ Group of words
√ makes sense
× have a meaning but an incomplete one.
PARTS OF A SENTENCE
PRACTICE EXCERCISE
Underline the subjects and circle the predicate-
1. I would like to drink a glass of juice.
2. Savitri has been cleaning the house since morning.
3. My brother watches T.V daily.
4. We are leaving for Delhi.
5. The monkey is sitting on the tree.
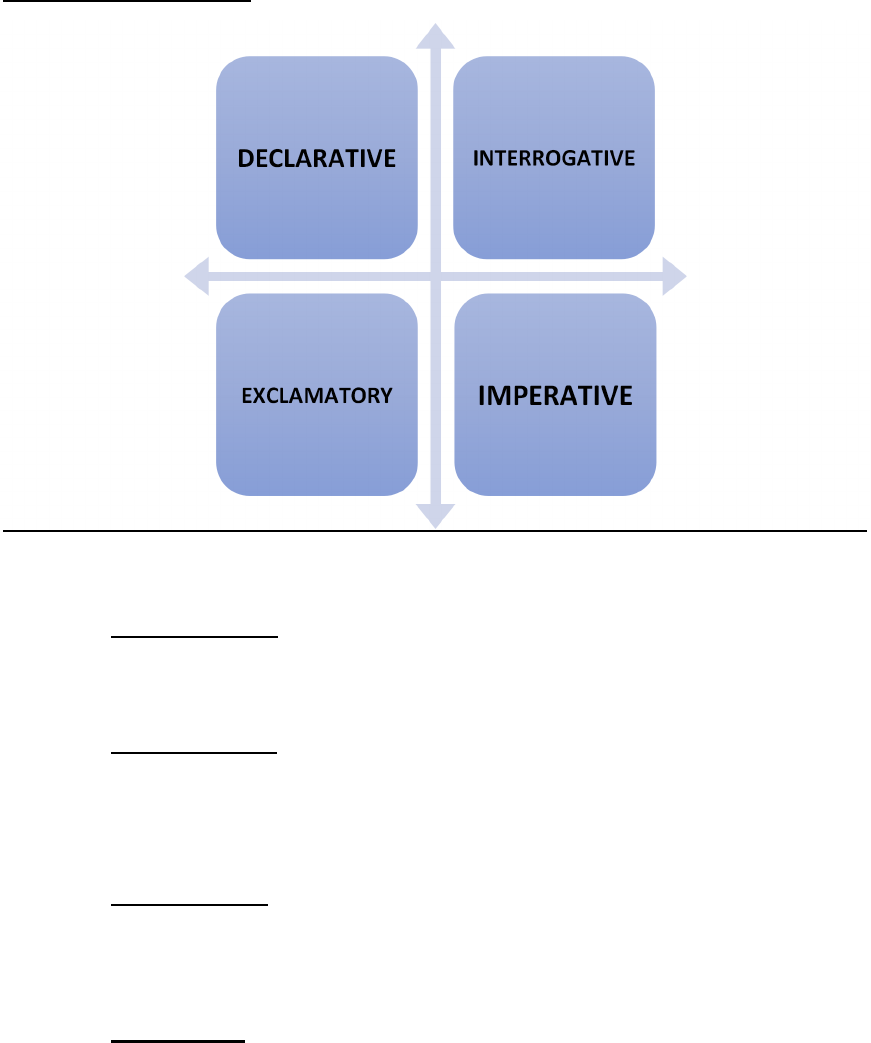
TYPES OF SENTENCES
1. DECLARATIVE: Sentences that declare or tell us about a fact or give
information. Eg. I go to school every day.
2. Interrogative: Sentences which ask a question. Eg. Why were you
late today? “?” this mark is identification for these sentences.
3. Exclamatory: Sentences which describe our feelings. Eg. Hurrah! We
won the match. “!” this mark is an identification of these types of
sentences.
4. Imperative: Sentences which indicate a request, a command, an
order, an advice or a suggestion are called imperative sentences.
Eg. Go and fetch me a glass of water (Order).
Please sit down and enjoy. (Request).
You should obey your elders. (suggestion)

PRACTICE EXERCISE-
Identify the types of sentences-
1. Kindly pass me some salt.
2. How long have you been living here?
3. May I help you sir.
4. Such a disgrace!
5. How are you going to Mumbai?

ARTICLES
Articles can be classified as-
English language has 26 alphabets.
VOWELS- a e i o u are vowels.
CONSONANTS- All the remaining letters apart from the above five are called
consonants.
Use of A/AN
A - Article A is used with consonants.
Ex- a house, a fan, a bridge, a frog
AN - Article an is used with vowels.
Ex- an elephant, an actor, an egg, an umbrella.
There are certain words that are followed by an despite of beginning with
consonants-
Ex- an hour (h is silent, sounds like a vowel)
A university (sounds like u, therefore is followed by a)
Indefinite
Articles
(A/AN)
Definite
Article
(THE)

USE OF THE
The Definite Article – THE
We use THE with:
1. A singular or plural noun when it is clear/obvious which person or thing we
are talking about.
2. Musical instruments (the violin, the guitar, the drums, the flute, the piccolo).
3. Something that is unique or there is only one.
the sun
the moon
the internet.
5. Names of rivers, seas, oceans, mountain ranges and deserts (always in
capitals).
The Ganga
The Black Sea
The Indian Ocean
PRACTICE EXERCISE
Fill in the blanks with a/an/the
1. ________ Lion is ______ king of ______ jungle.
2. _______ school is very clean.
3. Where is ______ class? They have _____ test today.
4. Children generally have _____ egg, ___ loaf of bread or ____ glass of
juice for breakfast.
5. We like to read ______ novel daily.

Homophones
Homophones are the words with same sound or pronunciation but with the
different spellings & meanings.
I went to the market. It was too hot outside.
The whole class talked about the hole in Karan’s pocket.
Waste Waist
Feet Feat
Loose Lose
Rode Road
Find Fined
Scene Seen
Son Sun
No Know
Stare Stair
Fare Fair
Too To
Whole Hole
There Their
Right Write
Tail Tale
Board Bored
Weak Week
Where Wear
Ad Add

Ate Eight
Sail Sale
Toe Tow
New Knew
By Bye
By Buy
Night Knight
Peace Piece
Eye I
Flour Flower
For Four
Great Grate
Heard Herd
Here Hear
Hi High
Bare Bear
Be Bee
Made Maid
Brake Break
Allowed Aloud
Hour Our
Scent cent
Complete the sentence with appropriate answers.
Give me an ______ to do this. (hour/our)
The ______ was strong. It hit me right in the head. (scent/cent)

The _______ of sheep grazed in the field. (heard/herd)
He said ____ to me. (hi/high).
I do not ______ the answer. (no/know)
Compound words
Compound words are formed by joining two words.
After + math = Aftermath
Butter + fly = butterfly
Some of the compound words are listed below.
Basket Ball Basketball
Base Ball Baseball
Rain Coat Raincoat
Back Bone Backbone

Back Pack Backpack
Life Time Lifetime
Up Stream Upstream
Dog House Doghouse
Week End Weekend
Earth Quake Earthquake
Bed Time Bedtime
With Out without
Identify the compound words from the list below.
Icecream, fashion, childhood, daylight,sidekick,earthquake, cyclone,
above, space, light, nowhere, earth, catfish, goldfish, arm, eyeball,
meanwhile, break, ache
Fill in the blank with the appropriate compound word.
The garden is full of ________.
The key got stuck in the ______.
The _______ is giving huge discounts on flight tickets.
I sat on the _______.
He loves _______ food.

Interjections
Read the sentences given below.
Oops! I made a mistake.
Bravo! What an excellent performance.
Yikes! Such a dirty road.
Wow! What an amazing scene.
The words like oops, bravo, yikes, wow represent emotions or sentiments.
They express sudden feelings of happiness, sadness, excitement, joy, surprise
or many more. Such expressions are called interjections.
Identify the interjections.
Ah! It hurts.
Eww! Don’t touch that.
Bingo! I got the answer too.
Grrr! Don’t piss me off.
Uh-oh! Help me please.

Aah Represents fear
Bingo Acknowledging the right thing
Wow Expresses surprise
Yay/ hurray Shows happiness/excitement
Shhh Used to indicate silence
Oops Used when a mistake is made
Yikes Fear/ concern
Fill in the blank with appropriate interjection.
______ I didn’t know that.
______ I am home.
______ what a pretty dress.
_____ we won the match.
______ I dropped my phone.

Prepositions
Read the following sentences.
Ria is hiding behind the curtain.
Shyam is going to office.
They are sitting on the chair.
All the words in bold show the place, time or position of the object.
Therefore, the words which determine the place, time or position of an object
are known as prepositions. They depict the relation of one thing with the
other.
Given below is the list of some common prepositions.
In
On
Under
Over
Below
Between
Among
Before
At
For
Behind
In
front
of
Inside
After
of
From
By
Towards
Near
Far
With Without

Identify the prepositions in the sentence given below.
The car was parked in front of the door.
The box was full of chocolates.
He sat on the chair.
His parents live in France.
He has his match from 5am to 12 noon.
Fill in the blanks with the correct prepositions.
I sat _____ Amit & Prashant.
The mangoes ____ the tree are ripe.
She is fond ____ sweets.
The lamp is kept _____ the table.
I am going ____ my car.
Types of preposition
Preposition of time
There are three prepositions which denote time. They are at,on,in.
Use of at
Denotes a specific point of time or a specific period/ occasion.
At 4pm.
At night
At the crack of dawn
Use of in
The preposition in is used with-
Seasons / months/ Year/ Parts of the day
In the morning

In summers
In 2010
Use of on
On is used with days & dates.
On Sundays
On 5
th
February
Preposition of position
In- (ex- in the room)
At- (ex- at the door)
On- (ex-on my desk)
Beside- (ex- beside the car)
Near- (ex- near my closet)
Behind- (ex-behind the scenes)
Preposition of movement & direction
To- (ex- to the hostel)
Towards –( ex-towards the clubhouse)
Into- (ex- into the well)
Down- (ex- down the hills)
Through- (ex- through the tunnel)

Fill in the blanks correctly.
The cat jumped ______ the well.
He ran ______ me.
She is sitting _____ the table.
I celebrate my birthday ______ January.
They went _____ locate the bus.

Conjunctions
Observe the sentences written below.
Mary and her mother go to the market.
The boy has a bat but not a ball.
Would you like to have tea or coffee?
I am not feeling well so I will take an off today.
The words and, but, or, because are joining two sentences. For instance,
Mary will go to the market. Her mother will go to the market. Instead, Mary
and her mother will go to the market.
A conjunction is a joining word used to join two or more sentences. It helps
in avoiding repetition.
Given below is a list of commonly used conjunctions
And
But
Because
So
Till
Until
Or
Yet
For
Neither
Nor
Either
Though

Although
FANBOYS is a commonly used acronym for coordinating conjunction.
F- FOR
A-AND
N-NOR
B-BUT
O-OR
Y-YET
S-SO
Identify the conjunction in the given sentences.
The boy was crying because he hurt himself.
It has been raining since yesterday.
Raman and his friend are going to watch a movie.
Although she was tired, she went for a walk.
Keep quiet or leave the room.
Fill in the blanks with suitable conjunctions.
______ childhood, I have played for my friends.
He is honest _____ impolite.
Mukesh loves eating green vegetables _____ he dislikes fruits.
He is studying ______ he has an exam.
Is this one yours _____ that one?
Types of conjunctions
There are three types of conjunctions.

Coordinating conjunctions (FANBOYS) are the conjunctions used to join or
link those sentences which are equally important and complete in itself.
Ex- Raghav and Rashi are friends.
He will have to take the medicines or he will fall sick.
Subordinating conjunctions are the ones which are used with dependent
clauses to complete the sentence.
Ex-
Although he has fever, he will attend the class.
You can do as you may like.
Conjunctions always existing in pair are known as correlative conjunctions.
Ex-
Neither did he learn his lessons nor did he attend his class.
Either have a sandwich or I will bake you a cake.

Adverbs
Adverbs tell us about a characteristic of a verb, adjective or another adverb.
The dog barked loudly.
(How did the dog bark?)
He came home late.
(When did he come home?)
The car is parked outside.
(Where is the car parked?)
The answers to all the questions given above are adverbs. Adverbs answer
the question of how, where & when.
The adverbs which answer the question how are called adverbs of manner.
She sang beautifully.
The team practiced thoroughly.
Ajay slept soundly.
The adverbs which answer the question where are called adverbs of place.
The bus came here.
We live there.
He is inside the house.
The adverbs which answer the question when are called adverbs of time.
The baby is sleeping now.
We will go to the cinema tomorrow.

Yesterday, was my birthday.
Identify the adverbs in the sentences given below.
Anu ran fast.
Kapil looked up in the sky.
I can’t find my register anywhere.
He played smartly.
He entered just now.
Fill in the blanks with suitable adverbs.
I met him _______.
Ishan can bowl _____.
My friend played ____.
He sat _____ the car.
I forgot my glasses _____.
List of some common synonyms.
Beautiful
Pretty
Start
Commence
Start
Begin
Stop
Halt
Build
Construct
Help
Aid,
assist
Rich
Wealthy
Silent
Quiet
Admit
Confess
Correct
Right
Evil
Bad
Exit
Leave
Legible
Clear
Final
End
Mend
Repair
Ordinary simple

