
Next Gen Internal Audit Analytics:
Continuous Monitoring &
Predictive Analytics
Joe Griglione – Director, Internal Audit
Theresa Bullock – Manager, Internal Audit Analytics
Zebra Technologies Corporation

Speaker Bios
Joe Griglione
Director, Internal Audit
Zebra Technologies Corporation
Theresa Bullock
Manager, Internal Audit Analytics
Zebra Technologies Corporation

Polling Question One
Question: How many session participants have ventured into continuous monitoring?
Question: Do you plan to integrate contintuous monitoring analytics into your 2024 audit plan?

Learning Objectives
1. Provide a roadmap of the internal audit analytics transformation from historical analysis to risk sensing
predictive analytics for attendees to apply within their organizations.
2. Offer practical insights into key stages of the analytics lifecycle while sharing actionable tips, strategies,
and methodologies to enhance the effectiveness of internal audit analytics.
3. Showcase real-world examples illustrating successful applications of historical analysis and predictive
analytics to demonstrate the impact on decision-making processes for internal audit and the business.
4. Explore the historic and predictive analytics insights that arise from tapping into the collective
intelligence of today’s participants to effectively leverage the diverse expertise within our field.

Establishing Foundations:
“Crafting Vision and Purpose”
An analytics function is more than just the technical scripting and data
analysis………….it is important to establish ‘why’ and ‘what’ for your existence
Cross-Functional
Collaborations
Position as Trusted
Advisors to Business
Aligning Vision with
Business Goals
Cultivate a vision for IA analytics that emphasizes:
Then, establish purpose through a mission and corresponding objectives

Establishing Foundations:
“Crafting Vision and Purpose”
Internal Audit Automation Program Mission & Objectives
Key Program Objectives
Mission Statement
Internal Audit aims to further
leverage technology in support of
auditing tactical areas of the
business to provide smarter and
more comprehensive audit results
while freeing resources for strategic
and enterprise-risk focused auditing.
Efficiency
• Engagement of audit in key tactical
areas with increased frequency/
breadth (full population) and with
limited impact to resources
• Free up resources from tactical audits
to more strategic & top-risk areas
Value
• Engage real-time risk evaluation for
specific areas to drive business
conversation and/or future audits
• Provide for third-line of defense based
on historic activity
• Audit full populations of data and
smarter sample selections
• Shift audit to the predictive space
“WHY”
“WHAT”
Establishing Foundations:
“Technical Proficiency in Data Management”
Investing in effective data management practices promotes reliability and informs decision making.
Data Infrastructure
Governance
Policies and
procedures for
collection, storage,
and usage
Team roles and
responsibilities
Compliance with
governing standards
Quality Assurance
Process to assess and
improve quality
Identify and rectify
inconsistencies and
errors
Establish cadence
Security and
Compliance
Robust security
measures to protect
sensitive data
Regulatory
requirements and
best practices
Regular audits to
ensure compliance
Mapping
Understand data
relationships
Visual representations
to illustrate the flow
of data
Consistency and
accuracy of formatting
and relationships
Continuous
Improvement
Culture of continuous
learning and
improvement
Stakeholder feedback
to identify areas for
enhancement
Emerging
technologies and
trends

Developing Organizational Excellence:
“How We Will Execute”
Long term, sustainable results depend on having a methodology that is
transparent, all-encompassing and repeatable
Develop a multi-staged methodology with:
Owners/Stakeholders
Phases
Key Activities
Deliverables
Due Dates

Developing Organizational Excellence:
“Who Does What”
Realization of mission and objectives is dependent on identifying, defining and communicating
stakeholder engagement and responsibility
Merge methodology and RACI
R Responsible (The Doer)
A Accountable (The Buck Stops Here) -
One per process
C Consulted (Provider of Knowledge)
I Informed (Keep in the Know)
Sub-Function
Activity
ID Activities
A
u
d
i
t
C
o
m
m
i
t
t
e
e
C
h
i
e
f
F
i
n
a
n
c
i
a
l
O
f
f
i
c
e
r
A
u
d
i
t
e
e
C
h
i
e
f
A
u
d
i
t
E
x
e
c
u
t
i
v
e
I
A
S
r
.
M
g
r
I
A
D
a
t
a
A
n
a
l
y
t
i
c
s
A
d
v
i
s
o
r
I
A
D
a
t
a
A
n
a
l
y
t
i
c
s
S
t
a
f
f
I
A
M
a
n
a
g
e
r
/
S
e
n
i
o
r
B
u
s
i
n
e
s
s
A
n
a
l
y
s
i
s
M
I
n
f
o
S
y
s
t
e
A.01 Es tablishment of A nalytics Vision and Objectives I C A/R R I I I I I
A.02 Design and Maintenance of Team Structure IC A/RIII
A.03 Coordination and Alignment of Vision and Objectives w ith Business and IT Leadership Expectation I C C A/R R I I C C
A.04 Communication of Progress and Milestone Achievement to Audit Committee I C A/R R C
B.01 Alignment of Design Approach to V ision and Objectives ICCARI ICC
B.02 Selection of Business Functions and Processes f or Analytics C I C A/R I I I I I
B.03 Definition of Testing Points of View , Trends and Relationships for Analysis I I C A/R C C I C I
B.04 Survey Existence of Current Analytic Outputs CARCCC
B.05 Execution of Business Process Understanding CICRRAC
B.06 Definition of Data Fields Aligned to Testing Points of View CIARICC
C.01 Review of Functional Data Fields w ith IT IAR CC
C.02 Mapping of Data Requirements to Data Sources IAR CC
C.03 Ex traction and Delivery of Required Data II/CI/C RA/R
C.04 Ex planation of Data Extraction CIIIRA/R
C.05 Verif ication of Data Completeness CIARCR
D.01 Recommendations and Guidance over Use of A nalytics Tool CA I A
D.02 Ex ec ution of Data Analytics Test Objectives CA R C I
D.03 Verif ication of Analytics Output CCARCC
D.04 Communication of Analytics Output IIA/RRC II
E.01 Identification of Key Analytics Output f or Further Testing CA R C I
E.02 Follow up Around Selected Samples w ith Business CII/CCA/R
E.03 Documentation of Follow Up Results II A/R
E.04 Communication of New Analytics Testing Requirements IIAR RC
F.01 Preparation of Analytics Detailed Dashboards ARRI C
F.02 Preparation of Detailed Audit Report ARCR
F.03 Reporting of Sample Testing Results IAIIRI
F.04 Reporting to Auditee I A RCRC
F.05 Preparation of Executive Summary/Board Level Communications and Dashboards I C I A R R C C I
Analytics
Testing
Execution
Testing Follow
Up
Reporting and
Communication
Data
Identification
and Extraction
Analytics
Design and
Approach
Strategic Vision
and Objectives
Methodology Phases
Methodology Activities
RACI by Activity by
Stakeholder
Stakeholders

Developing Organizational Excellence:
“Who Does What”
Info Systems /
Financial
Systems Leader
Business
Analysis
Manager
IA Manager /
Senior
IA Data
Analytics
Staff
IA Data
Analytics
Advisor
IA Sr.
Mgr
Chief Audit
Executive
Auditee
Chief
Financial
Officer
Audit
Committee
ActivitiesActivity IDSub-Function
IIIIIRA/RCIEstablishment of Analytics Vision and ObjectivesA.01
Strategic Vision and
Objectives
IIIA/RCIDesign and Maintenance of Team StructureA.02
CCIIRA/RCCICoordination and Alignment of Vision and Objectives with Business and IT Leadership ExpectationA.03
CRA/RCICommunication of Progress and Milestone Achievement to Audit CommitteeA.04
CCIIRACCIAlignment of Design Approach to Vision and ObjectivesB.01
Analytics Design and
Approach
IIIIIA/RCICSelection of Business Functions and Processes for AnalyticsB.02
ICICCA/RCIIDefinition of Testing Points of View, Trends and Relationships for AnalysisB.03
CCCRACSurvey Existence of Current Analytic OutputsB.04
CARRCICExecution of Business Process UnderstandingB.05
CCIRAICDefinition of Data Fields Aligned to Testing Points of ViewB.06
CCRAIReview of Functional Data Fields with IT C.01
Data Identification and
Extraction
CCRAIMapping of Data Requirements to Data SourcesC.02
A/RRI/CI/CIExtraction and Delivery of Required DataC.03
A/RRIIICExplanation of Data ExtractionC.04
RCRAICVerification of Data CompletenessC.05
AIACRecommendations and Guidance over Use of Analytics ToolD.01
Analytics Testing
Execution
ICRACExecution of Data Analytics Test ObjectivesD.02
CCRACCVerification of Analytics OutputD.03
IICRA/RIICommunication of Analytics OutputD.04
ICRACIdentification of Key Analytics Output for Further TestingE.01
Testing Follow Up
A/RCI/CICFollow up Around Selected Samples with BusinessE.02
A/RIIDocumentation of Follow Up ResultsE.03
CRRAIICommunication of New Analytics Testing RequirementsE.04
CIRRAPreparation of Analytics Detailed DashboardsF.01
Reporting and
Communication
RCRAPreparation of Detailed Audit ReportF.02
IRIIAIReporting of Sample Testing ResultsF.03
CRCRAIReporting to AuditeeF.04
ICCRRAICIPreparation of Executive Summary/Board Level Communications and DashboardsF.05

Developing Organizational Excellence:
“Set Milestones; Keep Accountability”
Ensure success by charting an incremental path and schedule regular touchpoints with
management (i.e. CFO, CAE, VPs, etc.) to report status of program progress
Timebound tasks on a roadmap
Dashboard status and broadcast
accomplishments

Embed Continuous Improvement:
“Lookback, Assess and Adjust”
Drive year over year progress through postmortem analysis; have a vision for your analytics'
program maturity and set goals and action plans accordingly
Leverage a maturity model
to help frame analytics
program current state vs.
desired state on multiple
dimensions
* “Internal Audit Analytics Maturity Model”, 2022, Author Unknown

Establishing Foundations:
“Upscaling Team Members”
Unlocking the potential of your team's analytical skills is within reach through…
Excel
Looker\Power BI
HR Data
T&E/PCard Data
Galvanize IA Analytics
Analytics Best Practices
Excel VBA
Power BI DAX
Center of Excellence
Business Intelligence
HR Analytics
Marketing Analytics
Continuous
Learning
Encouraging Innovation
Foster a culture of
experimentation and risk
taking
Access to Resources & Tools
Utilize available tools and
data sources inherent to IA
or the enterprise
Training and Development
Allocate time in
development plan for
relevant training
Cross-Functional
Collaboration
Identify analytics teams in
your organization to foster
a knowledge sharing
relationship.

Polling Question Two
Question: How many session participants have ventured into predictive analytics?

T&E
PCard
Wires
P2P
AP
Supply
Chain
Risk
Assessment
Supplier
Review
Network
Security
Compliance
Monitoring
Distributor
Risk
Strategic Analytics Partnerships
Becoming a trusted advisor through internal audit continuous monitoring analytics involves demonstrating
expertise, providing valuable insights, and building strong relationships with stakeholders.
Develop Expertise: Stay updated
with industry trends, best practices,
and emerging tools in data analytics
and audit methodologies.
Understand Business Objectives:
Understand the key risks,
challenges, and opportunities faced
by the business to tailor your
analytics initiatives accordingly.
Collaborate with Stakeholders:
Engage stakeholders in the audit
process, solicit their input and
feedback, and address their
concerns proactively.
Provide Actionable Insights:
Focus on delivering value-added
insights that help improve
business processes, enhance
controls, and optimize
performance.
Communicate Effectively: Tailor
your message to the audience's
level of understanding and
priorities. Use data visualization
techniques to convey complex
information effectively.
Build Trust and Credibility:
Establish trust and credibility with
stakeholders through
transparency, integrity, and
professionalism. Demonstrate
your commitment to objectivity,
independence, and ethical
conduct in all audit activities.

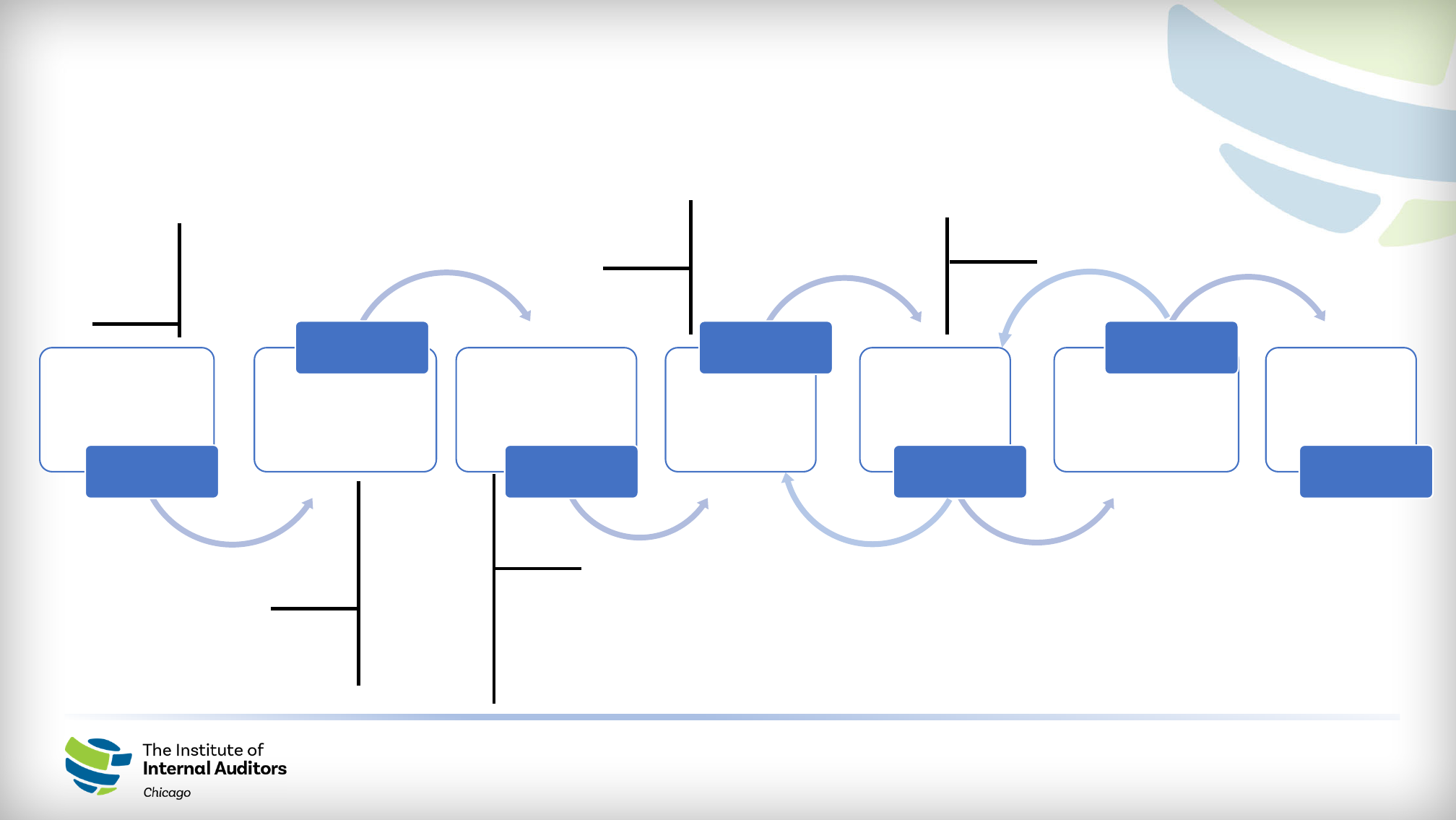
Becoming a Trusted Advisor through Continuous Monitoring:
“Continuous Monitoring Platform Lifecycle”
Building the bedrock of our continuous monitoring program in support of internal audit and the business.
Testing Follow-
Up
Analytics
Design and
Approach
Data
Identification
and Extraction
Analytics
Testing
Execution
Reporting and
Communication
Our Methodology
1 2 3 4 5
2
Weeks
4
Weeks
3
Weeks
3
Weeks
3
Weeks
15
Weeks
Analytics
Testing
Scope
BPO
Walkthroughs
Detailed
Testing by
Audit Team
Audit
Report

Policy Compliance
1. Spend over Credit Limits
2. Split Transactions
3. Missed Capitalization
4. Significant Credit Limit Changes
5. Inclusion & Diversity Statistics
Fraud, Waste, and Abuse
6. Higher Risk Merchant Classification Codes (MCCs)
7. Expenses by Terminated Employees
8. Expenses by class of transaction, function
9. Expenses by merchant, MCC (possible lost
volume discount opportunity)
10. Duplicate Transactions (including w/ T&E)
11. Weekend / Holiday Transactions,
12. Unusual P-Card Expense Locations
13. Average Monthly Spend Compared to Credit Limit
14. Dormant and/or Seldom Used Cards
6. Significant Spend Increases (MoM and QoQ)
7. Ghost Cards
Cardholder Administration
15. Terminated Employees w/ Active PCards
16. Credit Limits Not in Line w/ Employee Role
17. Duplicate Cards, Multiple Cards per Employee
18. Employees Who Also Hold a T&E card.
19. Shared Cards
20. Missed PCard Rebate Opportunities
*Beneficial Analytics per the Business Group
Becoming a Trusted Advisor through Continuous Monitoring:
“Continuous Monitoring Platform Scoping: Purchase Card Program”

Becoming a Trusted Advisor through Continuous Monitoring:
“Navigating Limitations”
Your team's adaptability and agility hold the keys to overcoming inevitable limitations.
Business
Disinterest
• Understand Business Goals
• Define Key Performance Indicators
• Communication and Collaboration
• Focus on Delivering Value and Driving
Tangible Outcome for the Organization
Data Disparity
& Access
Resource
Bandwidth
Constraints
• Centralized Data Repository
• Data Catalogue
• Data Standardization
• Identify Established Analytics Teams
Across Organization to Share Mature Data
Sources
• Consistency and Completeness of Data and
Process Mapping
• Project Pipeline (Effort/Complexity/Value)
• Auditor Assistance Part Time
• Identify Inefficiencies in Process
Managing Disinterest
Optimizing Resources
Enhancing Accessibility

Becoming a Trusted Advisor through Continuous Monitoring:
“Key Learnings in Continuous Improvement”
Annual post-mortems of methodology are vital for insightful forward planning, ensuring alignment with the evolving
maturity of capabilities, and optimizing future strategies.
Testing Follow-Up
Analytics Design and Approach
Data Identification and Extraction
Analytics Testing Execution
Reporting and Communication
The Evolution of Our Methodology
Continuous Monitoring Cadence
Initial acquisition and disparity
of data required the addition of
2 weeks to phase
2021
2022
2021
2023
Balancing our bandwidth to
sustain established CM projects
and continue to innovate
To prioritize stakeholder alignment
and reduce rework in the reporting
phase, additional readouts were
added between phases
To reduce the reporting phase
timeline, investigating the use of
generative AI
Concentrate on a narrower set of
tests to enhance our ability to
execute them effectively.
2022

Becoming a Trusted Advisor through Continuous Monitoring:
“Key Learnings in Continuous Improvement”
Balancing our bandwidth to
sustain established CM projects
and continue to innovate
Innovation
Maintenance

Introduction to Predictive Analytics:
Grey Market Sales Prediction
Shift auditing perspectives from being artifact and historical driven to forward looking insights
that help a company anticipate and plan for risk
What is Grey Market? What is current solution?
What are advantages of predictive analytics?
Authentic product
sold out of a low-cost
territory to a high-cost
territory thereby
disrupting distributor
business and profits
Manual “secret-
shopper” purchasing
that detects (and reacts
to) grey market
product already in the
market.
1. Shift the control from being manual and
detective to preventive and automated.
2. Insight is now forward looking instead of
historical.
3. Tedious manual efforts are eliminated;
investigations can be targeted based on
analytic output.

Introduction to Predictive Analytics:
Grey Market Sales Prediction
Areas that lend well to predictive analytics have a) suspected multiple variables impacting
another variable, b) adequate data capture, and c) governance around data input
Step 1: Profile identified instances
of grey market through region’s
manual efforts
- sku: TC77
- Quantity: 500
- Discount: 40%
- Country: Poland
- Reseller: A&B Inc.
Distributor 1
Distributor 2
- sku: TC77
- Quantity: 200
- Discount: 30%
- Country: Turkey
- Reseller: X&Y AG
Step 2: Assemble statistical
model with known model
variables
Step 3: Load quarterly sales out
and PC data, etc.; execute
statistical model
Step 4: Select predicted
output for further
examination
Average
Quantity
SKU
Average
Discount
%
grey
Quantity
PC Discount
Point of Sale (PoS) Report
End User Report
Deal 123456
Reseller
UK

Introduction to Predictive Analytics:
Grey Market Sales Prediction
The Evolution of Our Methodology Continues to Adapt : Machine Learning Lifecycle
•Work with business
to identify
established analytics
and opportunity for
enhancement
Advanced
Analytics Design &
Approach
•Assessment of
available data
•Import, Clean,
and Prepare Data
Data Collection
& Preprocessing
•Evaluation of features
•Alignment of features
•Assessment of various
model's metrics
Model
Selection
•Baseline
Accuracy
•Incorporation of
testing data
Model
Training
•Assess results for
reasonableness
•Compare to real
world data
profile
Evaluation &
Performance
Tuning
•Work with business to
test results in real
world scenarios to
validate accuracy
Validation
•Establish cadence
with business
•Integration into
established tools
Deployment &
Integration
•Sales Ops Team
Secret Shopping
Program
•Marketing Analytics
Advanced
Analytics Design &
Approach
•Global Secret
Shopping Data
•1,500 Investigations
•Sales Out Data
Data Collection
& Preprocessing
•Applied 7 Different
Models
•Applied 2 Different
Approaches
Model
Selection
•Aligned 5
Unique Features
•Included 2
variables
Model
Training
•Identified
XGBoost Model
with additional
2K “no violation”
sales from SO
Evaluation &
Performance
Tuning
•Working with SS
Program and IA Team
to test identified sales
in real world
Validation
•Pending
Validation Phase
Results
Deployment
& Integration
Introduction to Predictive Analytics:
Grey Market Sales Prediction
The Evolution of Our Methodology Continues to Adapt : Grey Market Predictive Platform Lifecycle
500 “No Violation” = 1
500 “Violation” = 2
500 “No Determination” = 3
Approach 1: Variables 1,2,3
Approach 2: Variables 1,2
Models: XGBoost, CatBoost, Random
Forest Classifier, K Neighbors Classifier,
etc…
Features: Origin Country,
Discount, Distributor, SKU,
Partner, Violation Indicator
Overall Accuracy: 92%
F1 Score Violation Indicator 1 : 80%
Cross-Functional
Collaboration
with Marketing
in Databricks

Introduction to Predictive Analytics:
Grey Market Sales Prediction
Lessons Learned on How to Avoid Pitfalls
Overfitting and Underfitting
Risky models that are either
to complex (over) or to
simplistic (under)
Imbalanced Data
Challenge when one variable
is significantly more prevalent
than other variables
Model Complexity
Trade-off between model
accuracy and interpretability.
Simplicity vs. Accuracy
Ethical Concerns
Mindful of ethical
considerations related to data
privacy, bias, and fairness
K-Fold Cross Validation
Training Data Adjustment
Based on Reasonableness
Baseline Accuracy and
Feature Importance

Introduction to Predictive Analytics:
“Grey Market Sales Prediction: Distributor Risk Assessment”
• Near Term: Support Zebra’s Internal Audit team in selection of distributor
audits and subsequent sample transactions for testing
• Medium-Term: Support Zebra’s secret shopping team by enabling smarter
sample selections
• Long-Term: Enable Zebra sales team to identify grey market transactions
prior to close of sale/shipment – Shift efforts from detective to preventive

Polling Question Three
Question:
Within different industries, what examples would lend themselves well to predictive analytics?
Ideas for Inspiration:
Healthcare: "How can
predictive analytics improve
patient outcomes and optimize
healthcare delivery?
What predictive models could
help in early disease detection
or personalized treatment
plans?"
Manufacturing: "How can predictive analytics
optimize production processes and minimize
downtime?
What predictive maintenance models could help
anticipate equipment failures?"
Finance: "How might predictive analytics mitigate
financial risks and improve investment strategies?
What models could help detect fraudulent activities
or predict market fluctuations?"
Retail: "In what ways can
predictive analytics
enhance customer
experience and increase
sales?
How can we predict
consumer trends or
forecast demand more
accurately?"
Telecommunications: "What
predictive analytics solutions
could enhance network
performance and customer
satisfaction?
How can we predict network
outages or anticipate bandwidth
requirements?"
Transportation: "What predictive
analytics solutions could enhance
logistics and supply chain efficiency?
How can we predict traffic patterns or
optimize route planning?"

Key Takeaways
1. Establishing Foundations
• Craft a clear vision for IA analytics that aligns with business goals, emphasizing cross-functional collaborations and the
role of audit as trusted advisors.
• Development of a repeatable and transparent methodology that encompasses data management and enhancement of
auditor capabilities is achievable.
2. Becoming a Trusted Advisor Through Continuous Monitoring
• Leverage analytics to establish meaningful business partnerships in support of IA and the business.
• Recognize and address challenges proactively and allow your methodology to evolve.
• Maintain a balance between sustained upkeep of established continuous monitoring projects and consistent innovation.
3. Introduction to Predictive Analytics
• Continued advancement of auditor capabilities and collaboration with seasoned analytics teams within your
organization is essential.
• Training data should reflect the real world, align features, create variables, balance your model between simplicity and
accuracy.

Section Break
